Freight transport is a big part of everyday business, from local lorry runs to huge shipments across the world. It’s what keeps shelves stocked, factories supplied, and goods flowing between buyers and sellers.
In this guide, we’ll define freight clearly, explore how transport works across different modes, and look at why it matters to your operation.
What we’ll cover
Fleets, bookings, subcontractors, compliance & payments.
With HX, you can manage them all in one place.
What is freight transport?
To put it simply, freight transport is the movement of goods from one place to another. It covers everything from raw materials to finished products, moving by road, rail, air, or sea. If it’s not people and it’s in transit, it’s probably freight.
Freight transport plays a big role in local and international trade. Whether it’s big rigs hauling pallets across Europe or containers on a cargo ship, the goal is to get goods from A to B, safely and on time. It’s often the link between manufacturers, warehouses, and retailers.
Key differences between freight and transportation
It’s easy to mix up the terms, but there’s a difference between freight and transportation. When you define freight, you’re talking about goods being moved, while transportation is the act or method of moving them. In short: freight is what’s moved, transport is how.
You’ll find that some businesses use the terms interchangeably. However, understanding the distinction is handy when working with different suppliers or reading contracts. For example, a transport service might cover people, while freight services are only about goods.
Resources like logistics glossaries and industry blogs help break down these terms for newcomers. The good news? The more time you spend in the sector, the more useful it is to speak the language clearly.
Types of freight transportation
There’s more than one way to move freight, and each method has its own advantages and drawbacks. The best choice depends on distance, cost, speed, and the type of goods you’re shipping.
Let’s take a look at the main options:
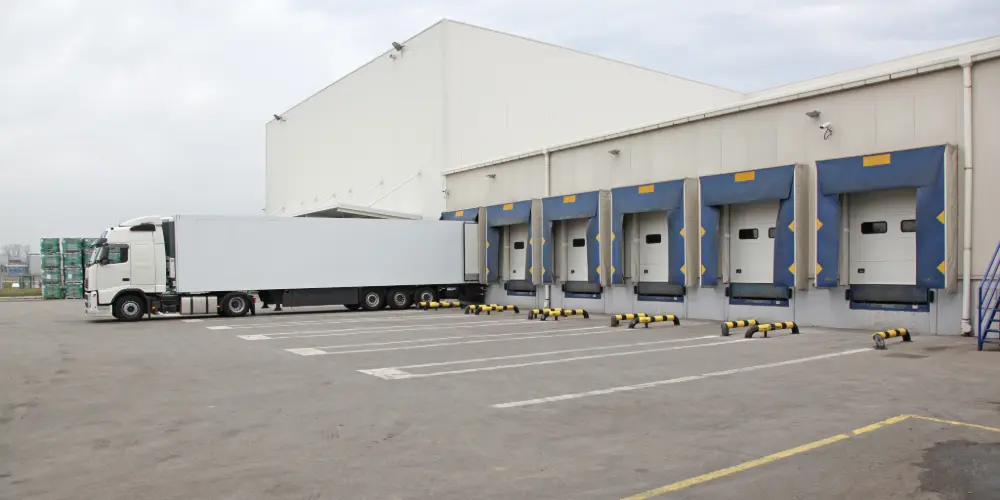
Road freight
Road freight is one of the most common forms of freight transport in the UK. If you’re just starting a haulage company, road freight is often the easiest place to begin, offering flexibility and lower startup costs compared to other modes. Lorries, vans, and articulated trucks carry everything from parcels and pallets to concert sound stages and cold chain logistics cargo.
Road freight also offers a huge variety when it comes to vehicle size and load capacity. From same-day couriers in vans to HGVs transporting pallets across the country, road transport can be scaled to suit almost any job.
If you define freight in this context, it’s often about flexibility: matching the right vehicle to the cargo and route.

Pros:
- Great for door-to-door service and rural delivery
- A wide range of lorry sizes to choose from
- Shorter transit times for domestic routes
- Easy to schedule and track
Cons:
- Affected by traffic, road conditions, and driver shortages
- Not ideal for long-distance international freight
- Higher emissions than rail or ocean freight
- Without the right strategy, fleet fuel consumption can be costly
Rail freight
Rail freight is a solid option for moving large volumes across long distances.
It’s more fuel-efficient than road and works well for heavy goods like minerals, steel, or containers. Many operators also use haulage vehicles to complete the first or final leg of rail journeys, with return loads helping reduce empty mileage and wasted time.
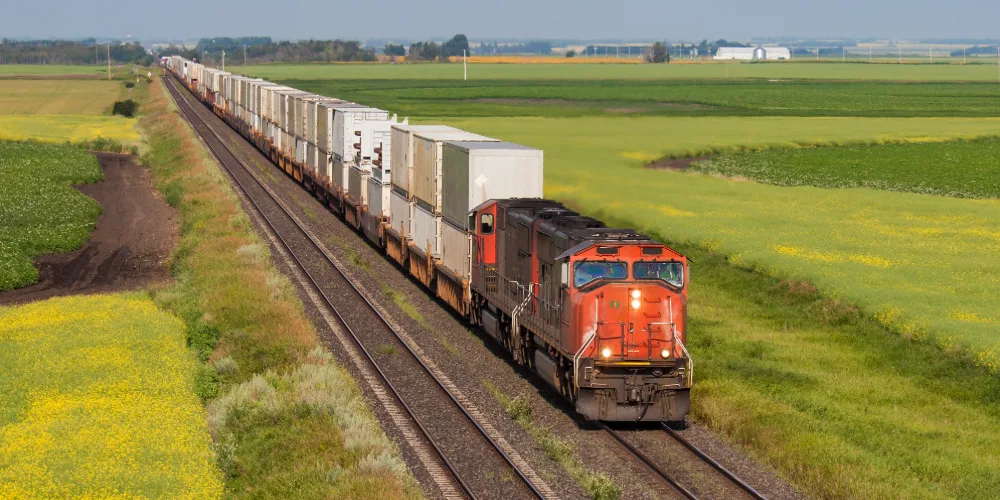

Rail is regularly used to connect key freight terminals, ports, and industrial hubs. It’s ideal for scheduled shipments that don’t require rapid delivery but benefit from scale and fuel efficiency.
As sustainability in logistics becomes more important, rail is gaining traction with companies looking to reduce their road mileage.
Pros:
- Lower environmental impact
- Ideal for heavy or bulk transport
- Reliable for scheduled long-haul routes
Cons:
- Limited by track access and terminal locations
- Still requires road transport at the start and end
- Less flexible for last-minute changes
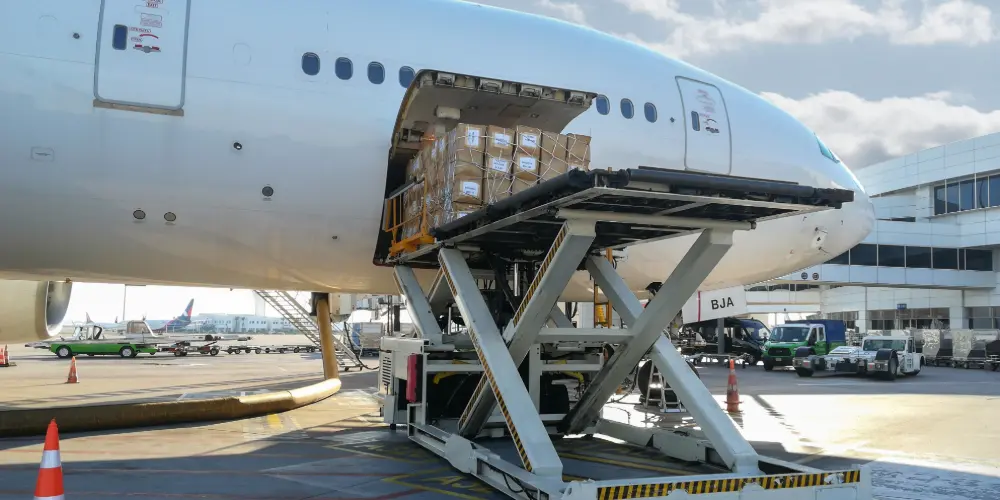
Air freight
Air freight is the fastest way to move goods, especially internationally. It’s commonly used for high-value, urgent, or time-sensitive cargo. Some businesses use freight exchanges to quickly match their shipment with available air capacity when deadlines are tight.
Air is especially valuable for global supply chains dealing with rapid turnover and tight lead times. Industries like pharmaceuticals, tech, and luxury goods often depend on fast and secure delivery. Though costly, the ability to avoid customs clearance bottlenecks and provide accurate ETAs gives it a major edge.

Pros:
- Fast delivery (great for emergencies or perishables)
- High security and low risk of damage
Ideal for international shipments with tight deadlines
Cons:
- Expensive compared to other options
- Limited space for bulk goods
- Higher environmental impact
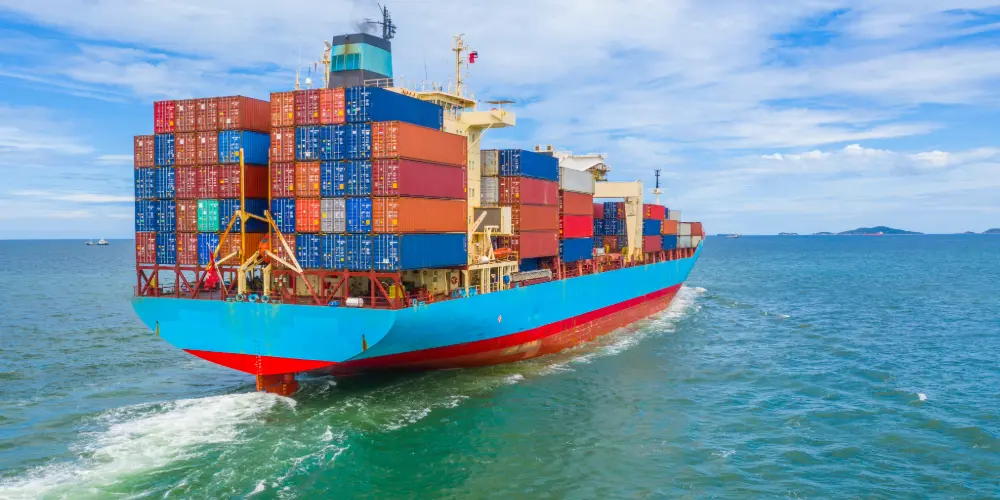
Ocean freight
Ocean freight is the go-to method for international trade. It’s slower than other methods, but it can carry massive volumes at a lower cost per unit. Most global freight transport shipping is done via container ships.
Shipping lines also offer options like groupage (shared containers) or full container loads, depending on your cargo volume. This makes ocean freight surprisingly accessible, even for smaller exporters or seasonal businesses. For companies asking “what’s freight” in international terms, sea transport is often the most cost-effective answer.

Pros:
- Cheapest way to ship large quantities around the world
- Suitable for bulky or non-perishable goods
- Global port network makes it accessible
Cons:
- Slow transit times and expensive
- Risk of delays from weather or port congestion
- Requires extra logistics for inland transport
The many types of shipping containers
Sea and rail freight are all about containers. These are standardised units that make loading, unloading, and transferring goods far more efficient.
There are several types, each suited to different kinds of cargo:
- Standard dry containers: These are the most widely used and come in 20- and 40-foot sizes. They’re ideal for general cargo like boxes, pallets, and non-perishable goods.
- Refrigerated containers (reefers): Designed for temperature-sensitive goods, reefers keep items like food and pharmaceuticals cold throughout the journey.
- Flat rack containers: Built for oversized cargo that doesn’t fit inside regular boxes. These have collapsible sides and are used for things like vehicles or machinery.
- Open top containers: Used for tall cargo that needs to be loaded by crane. They’re great for items like timber, scrap metal, or awkwardly shaped equipment.
- Tank containers: Made for transporting liquids, from chemicals to food-grade oils. These are cylindrical tanks housed in a rectangular frame for safe stacking and shipping.
Choosing the right container helps reduce damage, avoid delays at ports and cargo rail stations, and keep logistics running smoothly.
For most businesses, standard dry containers do the job. Specialised containers, however, offer extra flexibility when the cargo demands it.
Tips for managing freight risks and logistics
Freight doesn’t always move as planned! There are plenty of risks to manage along the way.
Delays, damaged goods, theft, and customs hold-ups are all part of the job, which is why having reliable systems and good logistics partners matters.
Using tools like GPS tracking or digital platforms can help you stay informed in real time. If something goes wrong, you’ll be able to communicate updates quickly and keep things on course. Working with experienced freight forwarders can also reduce admin load and help you navigate customs more smoothly.
Insurance plays a big role too, especially when you’re shipping internationally or handling high-value cargo. Many large haulage businesses build in risk assessments and audits to catch problems before they escalate. Whether you’re running a tight domestic route or a multi-leg journey, being proactive makes all the difference.
How freight forwarders fit in
Freight forwarding adds another layer to the transport process.
While freight moves physically from place to place, forwarders handle everything behind the scenes: finding and scheduling haulage carriers, sorting documentation, and coordinating across different transport modes. They’re often the ones making sure goods clear borders smoothly and arrive on time.
This role is especially useful in global logistics, where timing, regulations, and multi-leg shipments need careful coordination.
Forwarders don’t move the freight themselves, but they manage the journey from start to finish. They’re a key part of the supply chain process, particularly when dealing with cross-border requirements or time-sensitive goods.If you’re new to the industry, it helps to understand how forwarding fits into broader transport services like haulage.
Knowing who does what helps you plan better, avoid delays, and communicate more clearly with clients. Whether you’re shipping one crate or a full container, having the right people in your corner can make things run much smoother.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 4 main types of freight transportation?
The four main types are road, rail, sea, and air. Each comes with its own pros and cons depending on distance, speed, budget, and the type of goods you’re moving. Most companies use a mix of these depending on their needs.
What is the meaning of freight transport?
Freight transport means moving goods, rather than people, from one place to another using trucks, trains, ships, or planes. It’s a key part of supply chains, helping businesses get products where they need to be. If you define freight, it’s basically bulk cargo being moved around to meet demand.
What is the meaning of shipping transport?
Shipping transport refers to moving goods by sea using cargo ships and containers. It’s one of the most common ways to handle large international deliveries. This type of freight transport is slower than air but way cheaper when you’re moving high volumes.
Is freight the same as trucking?
Not quite. Freight is the goods, while trucking is one way of moving it, usually by road. So, while all trucking is freight transport, not all freight is moved by truck.




