- How we help you
Freight Focus
Your source for logistics knowledge and market updates
The UK’s logistics sector is booming, and with growth comes opportunity. Whether you’re driving freight, directing fleets or managing multi-channel supply chains, logistics offers a wide range of high-paying roles for skilled professionals.
In this guide, we’ll break down the top-paying logistics jobs in the UK, explore why certain roles command higher salaries, and show you what qualifications, experience and specialisations can help you earn more.
From coach driver salary ranges to strategic supply chain leadership, we’ll cover the full spectrum of roles in today’s logistics industry.
What we’ll cover
Fleets, bookings, subcontractors, compliance & payments.
With HX, you can manage them all in one place.What logistics covers and why certain roles pay more
Logistics covers everything from transportation and warehousing to supply chain strategy, procurement and analytics. Pay scales rise quickly as roles become more strategic, tech-driven or require high compliance and planning expertise.
Specialised logistics jobs like customs management, cold chain logistics, and transport analytics tend to attract higher salaries. That’s because these roles demand deep knowledge, certifications, and experience that help businesses run efficiently and legally.
Some roles also involve greater risk, decision-making authority, or oversight of important national infrastructure. These added responsibilities often translate directly into higher compensation.
Salary snapshot for top logistics roles in the UK
Here’s a look at the average salary ranges across the UK logistics industry:
Role Average Pay (UK) Senior Band (London/Strategic) Coach Driver £27,000 – £36,000 £38,000+ Supply Chain Director £85,000 – £120,000 £130,000+ Logistics Manager £45,000 – £65,000 £70,000+ Transportation Manager £40,000 – £60,000 £65,000+ Warehouse & Ops Manager £35,000 – £55,000 £60,000+ Procurement Manager £45,000 – £70,000 £80,000+ Customs Compliance Manager £50,000 – £75,000 £85,000+ Logistics jobs with strategy, compliance or network responsibilities offer the most earning potential. Sector and region matter too – coach driver salary UK data shows earnings peak around London, airports and major hubs.
Top high-pay roles in logistics
The logistics sector includes a wide range of roles, but some stand out for their earning potential. These positions often involve strategic oversight, high responsibility or specialist knowledge that’s in short supply.
Chief or director of supply chain
These senior professionals oversee entire supply chains from sourcing to delivery. They handle large budgets, high-pressure decisions and international logistics strategy.
Salaries rise quickly for those leading multi-site or international operations. Many come from backgrounds in procurement or distribution before stepping into this leadership role.
Supply chain manager
They coordinate production, inventory, transport and procurement operations. Experienced managers can rise into six-figure roles with cross-border or multi-sector responsibilities.
Industries like manufacturing, defence and retail offer high salaries at this level. Many managers pursue certifications like CILT to boost earnings.
They also play an important role in sustainability and cost control, often tasked with implementing greener transport options. As supply chains grow more complex post-Brexit, demand for experienced managers has increased across the UK.
Logistics or distribution manager
These logistics jobs manage warehouse teams, last-mile delivery and route optimisation. Pay increases significantly with scale, larger fleets, automated systems and complex delivery networks.
In e-commerce or 3PL sectors, bonuses and retention packages are common. Management software and people leadership are essential skills.
These managers often handle night shifts, cross-dock operations and returns logistics. Retailers and third-party providers rely on them to reduce delays and streamline delivery performance.
Transportation manager
This logistics job involves overseeing vehicle operations, HGV schedules and regulatory compliance. It’s a stepping stone to higher-paying fleet management and directorial roles.
You may also manage a team of drivers and negotiate contracts with hauliers. Those who have completed a become an HGV driver qualification often progress into these management roles.
They also guarantee compliance with driver hours, safety checks and DVSA regulations. Larger employers expect transport managers to lead digitisation and reduce fuel consumption across fleets.
Supply chain or logistics analyst
Data-focused logistics roles that analyse performance, optimise routing and reduce costs. These roles are rising fast in the logistics industry salary scale due to digitisation and sustainability efforts.
Most roles require strong Excel, SQL or ERP software skills. They often lead into planning or network design jobs.
Analysts are also responsible for creating dashboards, reporting KPIs and identifying inefficiencies across supply chain networks. With more companies relying on predictive analytics, this role continues to grow in demand and value.
Warehouse and operations manager
Operations managers handle staffing, inventory, KPIs, and safety compliance. Those in large depots, especially for retail or e-commerce, see higher bonuses and logistics salary growth.
Warehouses serving online retailers operate 24/7, so flexibility and workforce management are essential. Experience with WMS software and stock accuracy targets is also a major plus.
Procurement and purchasing manager
These logistics roles focus on sourcing goods, negotiating supplier contracts and reducing spend. Strategic procurement often links to board-level decision-making, increasing pay.
Leadership in this area is covered in more detail below. This role overlaps often with customs, finance and sustainability departments.
Customs and trade compliance manager
Experts in import/export law, Incoterms and trade regulations. They’re responsible for keeping operations legal and avoiding costly fines – and their salaries reflect this responsibility.
They often work closely with freight forwarders and government bodies. This role has grown post-Brexit and is in high demand.
Coach driver salary: A key role in UK logistics
A coach driver salary in the UK typically ranges from £27,000 to £36,000, depending on experience and route type. In larger cities or with private charters and tour operators, salaries may rise beyond £38,000.
To become a coach driver, you need a PCV licence, but what is that exactly? The PCV driver meaning refers to a “Passenger Carrying Vehicle” licence, which qualifies you to drive coaches or buses professionally.
So, how much do coach drivers earn compared to other transport roles? While not as high as logistics managers, coach drivers benefit from job security and regular overtime.
Here’s a breakdown:
- Base salary: £27,000 – £36,000
- With overtime: Up to £40,000+
- Private charters or tourism: Premium rates and bonuses
Many wonder how much does a coach driver earn with extra responsibilities like route planning or training. Those additional tasks can increase pay or lead to promotions into fleet management.
High‑earning specialist roles
In the logistics industry, certain specialist functions operate at the cutting edge of the supply chain, and command premium pay as a result.
These logistics roles typically involve a combination of niche expertise, strategic influence and high accountability, pushing their salary bands above standard operations roles.
Procurement and purchasing leadership
- Salary range: £50,000 ‑ £90,000 for senior managers, with director levels from around £75,000 up to £108,000+ depending on remit.
Senior procurement officers and heads of sourcing are among the highest paid delivery jobs UK wide. Their influence on cost-saving and supplier partnerships makes them top earners.
They often report directly to finance or operations directors. Pay is highest in sectors like manufacturing and defence.
Analytics and optimisation roles
- Salary range: £30,000 ‑ £45,000 for analysts; senior optimisation or network modelling roles can reach £50,000+ in some cases.
Data science and logistics combine in these positions – think supply chain analysts or network modellers. Strong Excel, SQL and supply chain system knowledge are important.
These professionals are essential for reducing costs and improving performance. They’re also valued in green logistics or carbon reporting.
Advanced data skills let them simulate distribution models, forecast inventory trends and streamline procurement. Many companies now consider this role mission-critical for competitive advantage.
Fleet and transportation management
- Salary range: £36,000 ‑ £70,000+ depending on size of fleet and region (London/multi‑site may drive higher pay).
Fleet directors often manage dozens or hundreds of vehicles, HGV compliance, and driver strategy. These roles overlap with coach driver salary trends – with management often earning double.
Leadership, route planning software and safety compliance are core skills. This role requires balancing operational efficiency with driver satisfaction.
Fleet managers also oversee vehicle acquisition, HGV insurance, servicing, and emissions compliance. Those operating across multiple depots can earn significantly more due to the complexity involved.
Specialisations with premium pay
Some areas of logistics require rare technical skills, high compliance standards, or advanced planning capabilities, and the pay reflects that.
These specialisations are needed for high-stakes operations and often lead to some of the best salaries in the industry.
Cold chain logistics
- Salary range: £45,000 – £70,000+
Cold chain logistics specialists make sure temperature-sensitive products (like vaccines or fresh food) stay within tight limits across the supply chain. Mistakes can cause catastrophic losses, making this a high-pressure, high-reward field.
Customs compliance
- Salary range: £50,000 – £85,000+
These managers handle cross-border documentation, tax rules and regulatory filings. Since Brexit, demand has surged in freight, e-commerce and global logistics sectors.
Network planning and logistics engineering
- Salary range: £50,000 – £80,000+
Network planners optimise where to place warehouses, how to route deliveries and how to reduce costs. They use modelling software and work closely with procurement and operations teams.
Career progression pathways in logistics
You don’t need to start at the top to reach high-paying logistics jobs. Many professionals move up from warehouse assistant to team lead, transport planner and eventually logistics manager.
Important steps include getting certifications, learning logistics software and moving into analytical or supervisory roles. With effort, it’s possible to move from entry-level operations into high-earning supply chain careers.
Those looking to switch logistics roles entirely can also explore how to start a freight forwarding company. These entrepreneurs often earn six-figure incomes.
Many start as admin assistants or route planners before specialising. With digital transformation accelerating, gaining software skills is often a faster route to higher pay than traditional pathways.
How to qualify: skills, certifications and experience
You don’t always need a degree to succeed in logistics. However, many high-paying logistics jobs require:
- Certifications: CILT UK, CPC, Lean Six Sigma, APICS
- Experience: Multi-site, international or regulated environments
- Skills: Data analysis, procurement negotiation, project management, HGV compliance, leadership
For coach or HGV roles, a valid licence and clean record are must-haves. Strategic roles, on the other hand, demand leadership, communication and strong commercial awareness.
To break into the field, start with entry-level logistics roles and work your way up. Logistics careers reward long-term development, hands-on knowledge and technical growth.
Find reliable carriers and cut your costs with Haulage Exchange
Sign upFrequently asked questions
Which logistics jobs pay the most in the UK?
Director-level roles like Supply Chain Director, Procurement Head, and Customs Compliance Manager top the list. These jobs carry high responsibility, strategic oversight and often multinational complexity.
Do I need a degree or will certifications and experience be enough?
You can progress without a degree, especially in operations or transport roles. Certifications like CILT, CPC or Six Sigma are widely accepted and often more practical.
Which industries offer premium pay for logistics roles?
Sectors like pharmaceuticals, defence, cold-chain logistics and e-commerce offer the highest pay. These industries deal with sensitive, high-value or fast-moving products.
Is London pay higher than the rest of the UK?
Yes – logistics salaries in London and major port hubs like Felixstowe or Southampton are typically higher. This reflects both demand and cost of living.
What skills move candidates into higher-pay bands?
Data analysis, compliance, negotiation and software expertise are in demand. Employers also value leadership, risk management and sustainability insight.
Which certifications help most for senior roles?
The most recognised are CILT (Chartered Institute of Logistics and Transport), Lean Six Sigma, and APICS CPIM. CPC is also all-important for transport and fleet-related leadership.
Can I move from warehouse operations into a higher-paying supply chain role?
Yes, many start as warehouse managers and move into analyst, procurement or logistics planning positions. Upskilling with software and analytics training helps that shift.
If you’re exploring a driving career or researching licence categories, you’ve probably come across the terms HGV and LGV. These acronyms cause plenty of confusion, especially when they seem to refer to the same type of vehicle.
In this guide, we’ll unpack the real HGV and LGV meaning, explains UK licence categories, and clears up the most common myths. Whether you’re planning to become an HGV driver or just trying to understand the differences, we’ll help you decode the terminology.
What we’ll cover
Fleets, bookings, subcontractors, compliance & payments.
With HX, you can manage them all in one place.What HGV and LGV mean today
Despite the different names, HGV and LGV now mean exactly the same thing in the UK. Both refer to vehicles over 3.5 tonnes used for commercial freight or heavy goods transport.
What does LGV stand for? LGV technically stands for ‘Large Goods Vehicle,’ not ‘Light Goods Vehicle’ as many assume, and this modern definition aligns with EU regulations that classify commercial goods vehicles by weight.
It’s important to note that many industry professionals still use both terms interchangeably. When searching for jobs, training, or legal information, you may see both HGV and LGV used in the same context, even though they legally refer to the same vehicle category.Why the terms changed in 1992
Before 1992, LGV meant Light Goods Vehicle, generally covering vans under 3.5 tonnes. HGV, on the other hand, was used for anything over that threshold.
After aligning with European directives, the UK updated its classifications. LGV was redefined to mean Large Goods Vehicle, and this brought it in line with the existing HGV category.
That means HGV and LGV now refer to the same group of heavier commercial vehicles, regardless of the brand of lorry. Despite the shift, the outdated meaning of LGV (as ‘light’) still creates misunderstanding today.
Common misconceptions about ‘Light Goods Vehicle’
Many people, including job seekers and even some employers, still think LGV refers to courier vans or small trucks under 3.5 tonnes. This misunderstanding persists in part due to the historical usage of LGV pre-1992.
In reality, vans under 3.5 tonnes fall into an entirely different licensing category. They’re often referred to as Category B vehicles, the same as standard cars.
If you’re looking at job ads or training courses and see ‘LGV,’ always check the context. Most of the time, LGV will mean the same thing as HGV: a vehicle above 3.5 tonnes.
Licence categories explained
There are several UK driving licence categories related to HGV vs LGV vehicles. These are determined by the vehicle’s weight and configuration.
Understanding the differences between them helps you figure out which type of lorry you can legally operate. Plus, it will also help you glean what kind of training you’ll need.
Category C (rigid lorries: up to 32 tonnes)
Category C licences allow you to drive large rigid-body vehicles over 3.5 tonnes, with a maximum authorised mass (MAM) of up to 32 tonnes.
These vehicles have a fixed cab and trailer, meaning they aren’t articulated. They’re commonly used for local deliveries and are often referred to in Class 2 terminology.
Category C+E (articulated lorries: up to 44 tonnes)
Category C+E licences allow you to drive articulated lorries, which have separate cab and trailer sections. These are the largest legal lorries in the UK, with weights up to 44 tonnes.
This licence is often considered the highest tier and opens the door to long-distance and high-capacity haulage jobs. You must first pass Category C before upgrading to C+E.
Category C1 (3.5–7.5 tonnes)
Category C1 lets you drive medium-sized vehicles between 3.5 and 7.5 tonnes. This licence is common for delivery drivers or specialist transport jobs such as horseboxes or ambulances.
If you passed your car test before 1997, you might already have this category included by default on your licence. A valuable perk, to be sure.
Class 1 and Class 2 vs modern categories
The terms Class 1 and Class 2 are still widely used in job descriptions, training centres, and even on fleet management sites. But these terms don’t appear on your driving licence.
They correspond to the current categories as follows:
- Class 2 = Category C (rigid lorries)
- Class 1 = Category C+E (articulated lorries
Although they’re technically outdated, Class 1 and Class 2 remain industry shorthand. So if you’re browsing training options or trying to become an HGV driver, be aware of both sets of terms.
Which licence do you need for different vehicle weights?
Here’s a quick breakdown to help you understand the weight ranges and the right licence to match:
Vehicle Type Weight Range Required Licence Van or pickup Up to 3.5 tonnes Category B Medium lorry 3.5 to 7.5 tonnes Category C1 Large rigid lorry Over 7.5 tonnes Category C Articulated lorry Up to 44 tonnes Category C+E Looking for more specific size thresholds and regulations? See our full guide on lorry sizes for more details.
How to qualify: medical, theory, practical and driver CPC
To drive HGV and LGV vehicles professionally, you’ll need more than just a licence. There’s a step-by-step process to qualify.
First, you’ll complete a medical exam to check for fitness to drive. Then you’ll need to apply for a provisional entitlement.
Next comes the theory test, which includes hazard perception and multiple-choice questions. Once you’ve passed, you can book your practical driving test for the appropriate category.
Finally, professional drivers must also complete Driver CPC (Certificate of Professional Competence) modules.
Typical costs to train and get licensed
Costs vary depending on the licence category and training provider, but here are general estimates:
- Medical test: £50–£100
- Theory test: £37
- Training course: £1,200–£2,000+
- Driver CPC: Around £300–£400
Some employers cover part of the cost for new drivers. Others offer apprenticeships or schemes to help reduce the financial burden.
Career paths for qualified HGV/LGV drivers
With an HGV or LGV licence, you can unlock a wide range of transport careers. Many start in local delivery or regional transport, then progress into higher-paying long-haul roles.
Others choose specialised fields like hazardous materials, refrigerated transport, or even international haulage. The category you’re licensed for will influence the roles available.
Outside the UK: How other regions label heavy vehicles
In the EU, the term LGV (Large Goods Vehicle) is used more often than HGV. It reflects the same categories but avoids the confusion with ‘light’ goods.
In the US, they use the term commercial motor vehicle (CMV) and classify trucks by class numbers: Class 7 and Class 8 being most similar to the UK’s HGVs. It’s helpful to be aware of these differences if you plan to work abroad or with international fleets.
Why job ads and training pages still use both terms
Even though the DVLA treats HGV and LGV as the same, the terms are used inconsistently across the industry. Some employers write “HGV/LGV” to cover all bases.
Training providers also do this for SEO reasons or to appeal to those who still remember the old meanings. That’s why it’s important to read the job or course description carefully.
Find reliable carriers and cut your costs with Haulage Exchange
Sign upFrequently asked questions
Do vans under 3.5 tonnes count as LGV?
No, despite the name, LGV no longer refers to Light Goods Vehicles. Vans under 3.5 tonnes fall under Category B, the same as standard cars.
Do I need Driver CPC for occasional or agency HGV work?
Yes, if you’re driving an HGV or LGV for commercial purposes, even just occasionally, you need a valid Driver CPC. There are some exceptions, but most agency roles will require full certification.
Can pre-1997 car licence holders drive 7.5-tonne vehicles?
Yes, if you passed your test before 1 January 1997, you likely have Category C1 entitlement on your licence. This lets you drive vehicles between 3.5 and 7.5 tonnes without extra testing.
What is the difference between HGV and LGV in the UK?
There isn’t one: HGV and LGV now refer to the same types of vehicles over 3.5 tonnes. The confusion arises from outdated definitions, but legally, the two terms are interchangeable.
The Autumn Budget is where the government sets out its annual financial plan — from tax rates to investment priorities and new digital requirements. While much of it applies broadly to UK businesses, haulage companies will feel the impact more sharply because of high operating costs, complex compliance, and the reliance on subcontracted drivers.
The Autumn Budget 2025 introduces a mix of rising costs, new digital reporting rules and updated tax allowances that will influence how haulage firms plan fleets, manage subcontractors and run their operations in the years ahead.
Here’s a clear breakdown of what will matter most for the haulage sector.
What we’ll cover
Fleets, bookings, subcontractors, compliance & payments.
With HX, you can manage them all in one place.Fuel duty and operating costs
Fuel is one of the biggest cost pressures in road haulage, and the 2025 Budget sets out a staged increase over the next two years.
Fuel duty reversal (2026–27)
The government will reverse the temporary 5p fuel duty cut in three steps:
Date Increase Meaning 1 September 2026 +1p First stage of duty returning to 2022 levels 1 December 2026 +2p Further rise in per-litre cost 1 March 2027 +2p Full reversal complete Alongside this:
- Vehicle Excise Duty for HGVs will rise with inflation from April 2026.
- The HGV levy will also rise in line with inflation.
What this means for haulage companies: across a fleet operating thousands of miles per day, even small increases will have a compounding effect on operating costs.
Fleet investment: trucks, trailers and yard equipment
Haulage companies typically plan fleet replacement years ahead. The 2025 Budget provides several tax allowances that will ease the cost of investment — especially helpful for replacing older units or expanding capacity.
Key allowances
Allowance Applies to Runs until Benefit 100% first-year allowance (FYA) Zero-emission HGVs 31 March 2027 Deduct full cost in year one 100% FYA EV charging infrastructure 2027 Full deduction on installation 40% first-year allowance Most new trucks, plant, yard kit From Jan 2026 Faster tax relief on major assets Why this matters for haulage:
High-value assets — tractors, trailers, refrigeration units, telematics, yard handling equipment — can be timed to optimise tax relief during the 2026–27 window.Income tax, NI and business taxation
Many haulage businesses operate as limited companies, and the Autumn Budget 2025 includes several changes that will affect both directors and payroll.
Key updates
- Personal tax thresholds will remain frozen until 2031 — increasing effective tax for rising wages.
- NI thresholds will remain frozen, impacting overall labour cost across drivers, planners and admin staff.
- Dividend tax rates will increase from 2026–27, affecting directors who draw income via dividends.
- Corporation Tax will remain unchanged, but allowances will play a bigger role in tax efficiency.
Impact:
Labour will become more expensive, and margins will tighten unless businesses offset this through efficiencies.Digital compliance, invoicing and subcontractor management
This is one of the most significant areas for haulage companies — not only because of their own reporting obligations, but because many rely heavily on subcontracted drivers.
The 2025 Budget confirms a shift towards stricter digital record keeping:
Key deadlines
- April 2027: penalties for late VAT and Self Assessment filings will become tougher.
- 2027: Making Tax Digital will expand, requiring more accurate digital records across the business.
- 2029: Mandatory e-invoicing will apply to all VAT-registered businesses.
For haulage companies working with subcontractors, this will matter because:
- Clean digital audit trails will become essential for VAT, accounting and haulage insurance reviews.
- Subcontractor invoices will need to be accurate, VAT-compliant and digitally consistent.
- Payment errors — especially across large subcontractor pools — will become more expensive under the new penalty regime.
How SmartPay will help haulage companies manage these changes
SmartPay will reduce admin for both in-house fleets and subcontracted drivers, supporting the tighter compliance landscape set out in the Autumn Budget.
1. Cleaner VAT and invoice checks
SmartPay will automatically validate key VAT details, helping reduce the risk of errors and mismatched subcontractor invoices — a major pain point for haulage operations handling high volumes of third-party work.
2. Standardised digital invoices (future-proofed for 2029)
With e-invoicing becoming mandatory in 2029, SmartPay already issues consistent, structured digital invoices. This will help haulage firms maintain clean audit trails across subcontractors.
3. One-click, consolidated payments
Instead of paying subcontractors one by one, SmartPay will allow a single bulk payment covering all approved invoices — ideal for haulage businesses with complex weekly payment runs.
4. Automatic reconciliation
Each invoice will be matched automatically to its payment, reducing manual admin, preventing duplicate payments and improving accounting accuracy ahead of stricter Making Tax Digital requirements.
5. Supporting MTD for Self Assessment
SmartPay and HX will continue working with accounting software providers to support the rollout of MTD for Self Assessment, making it easier for subcontractors to stay compliant — and for haulage businesses to receive clean, standardised digital invoices from them.
The result:
Less back-office pressure, fewer payment mistakes, faster subcontractor turnaround and a more compliant end-to-end workflow.HGVs and the road to decarbonisation
While the heavy truck market is still early in its transition to zero-emission vehicles, the Budget includes several long-term measures:
- Additional investment in charging infrastructure will be made.
- EV-only forecourts and charging sites will receive 10 years of business rates relief.
- The new EV mileage tax will apply to cars only — not HGVs.
Impact:
Little will change immediately for heavy haulage, but companies with depots will benefit from infrastructure and charging incentives when planning ahead.Depots, yards and multi-site operations
Haulage companies often manage multiple depots, yards, workshops and warehouses.
Changes in the 2025 Budget include:
- Small Business Rates Relief will be extended for companies operating more than one property.
- Long-term rates relief will apply to EV charging infrastructure installed on commercial premises.
- Site expansions and yard upgrades may become more cost-effective.
Cross-border and freight-specific changes
For operators running European or import/export work:
- Customs duty relief on low-value imports (under £135) will be removed by 2029.
- HMRC will expand real-time data matching, increasing scrutiny over mixed domestic/international freight income.
- Future tax conditionality may link compliance more closely to transport licensing.
Key takeaways for haulage companies
Here’s a summary of what’s changing with the 2025 Budget:
- Fuel and fleet operating costs will rise from 2026–27.
- Tax allowances will offer opportunities for fleet and yard investment.
- Digital compliance will tighten, especially for subcontractor-heavy operations.
- E-invoicing will become mandatory in 2029, requiring consistent digital invoices.
- SmartPay will help reduce admin, prevent payment errors and support haulage companies as the industry shifts towards fully digital workflows.
Find reliable carriers and cut your costs with Haulage Exchange
Sign upFrequently asked questions
How will the Autumn Budget 2025 affect haulage operating costs?
Fuel duty will increase in stages from 2026 to 2027, HGV road tax will rise with inflation and the HGV levy will also be uprated. These changes will increase the cost per mile for haulage fleets and subcontracted vehicles, making fuel budgeting and efficient payment processes more important.
What will the 2025 Budget mean for managing subcontractors?
Stricter digital reporting, tougher VAT penalties and future e-invoicing rules will place more pressure on haulage companies to maintain accurate, consistent records for subcontracted drivers. Clean, compliant invoices will become essential, and tools like SmartPay will help standardise subcontractor invoicing and reduce payment errors.
Will the 2025 Budget introduce new compliance requirements?
Yes. From 2027, Making Tax Digital will expand, and penalties for late VAT and Self Assessment filings will become tougher. From 2029, VAT-registered businesses will be required to use structured e-invoices. Haulage companies will need digital record-keeping systems capable of handling this shift.
How will SmartPay help haulage firms prepare for these changes?
SmartPay will support compliance through automatic VAT checks, structured digital invoices and one-click bulk payments to subcontractors. These features will help haulage companies maintain clean audit trails, reduce admin and stay aligned with the tighter reporting standards introduced in the Autumn Budget 2025.
When you’re spending long hours on the road, your cab becomes more than just a vehicle; it’s your workspace, your breakroom, and sometimes even your bedroom. Packing the right gear can turn a tough journey into a manageable one and help you avoid common mishaps.
In this guide, we break down the must-have HGV driver accessories and gear that everyone should have in their trucks. From emergency kits and tools to food supplies and personal hygiene gear, you’ll find everything you need to stay safe, comfortable, and ready for the long haul, or even to inspire bold ideas for lorry driver gifts.
What we’ll cover
Fleets, bookings, subcontractors, compliance & payments.
With HX, you can manage them all in one place.Safety and emergency kit
A solid emergency kit will help you handle injuries, breakdowns, and low-visibility conditions with confidence, making it a go-to section for anyone looking for practical gifts for lorry drivers.
First aid and PPE
No one plans to get injured on the job, but even a small scrape can become a hassle without the right supplies. A well-stocked first aid kit and basic personal protection equipment can make all the difference, especially on-site.
Keep a first aid kit that includes:
- Bandages
- Antiseptic wipes
- Plasters
- Painkillers
- and be sure to check expiry dates regularly.
If you’re visiting depots, construction zones, or ports; make sure you have:
- High-vis gear
- Steel-toe boots
- A hard hat
- Safety gloves
Some sites have their own PPE rules, so it’s worth carrying extra items just in case.
It’s not just about compliance; proper gear helps prevent injury in unpredictable environments.Breakdown and visibility gear
If you break down on a hard shoulder or in poor visibility, it’s your job to stay safe while you wait for help. That means being seen by other drivers and staying protected from the elements.
You should be carrying:
- A reflective jacket
- Warning triangles
- A torch or headlamp
- Spare batteries
Winter extras:
- Jump leads
- A high-grip mat
- An emergency foil blanket (can be lifesavers in freezing conditions)
- A portable tyre inflator or sealant helps with slow punctures if you’re miles from a garage)
- A high-vis vest (could be what keeps you safe at night or in heavy rain)
These are both top picks when shopping for HGV driver gifts with real purpose.
Tools and basic maintenance
Even if you’re not a trained mechanic, having a few tools can get you out of trouble. They help you fix minor issues before they turn into major delays.
You should always have:
- A small tool kit with pliers
- Screwdrivers
- An adjustable wrench
- Duct tape
- Zip ties
- WD-40
- A tyre pressure gauge
- Gloves for dirty work
Keep spare bulbs and fuses handy, especially if you’re driving long distances at night. A multi-tool or Swiss Army knife is also useful, you’ll be surprised how often it comes in handy, making it one of the top truck driver accessories.
Navigation, comms and documents
Staying on track and in contact is a big part of the job. A few small tools can help you plan better, stay legal, and avoid missed delivery windows.
An HGV-friendly sat nav is better than your smartphone when it comes to height, weight, and route restrictions. Make sure you also carry a phone charger or power bank to keep your devices topped up.
As you’ll read in any guide on how to become an HGV driver, you’ll need to keep a few things on you at all times.
This includes:
- Your driver CPC card,
- Tacho card
- Any required delivery documents on hand when you set off.
A simple clipboard or folder can also help you keep paperwork neat and ready for inspection. So, consider these as functional lorry driver accessories for day-to-day convenience.
Food, water and simple cooking
Eating well on the road isn’t just about saving money; it’s about feeling good and staying alert. A small setup can go a long way when you’re tired, hungry, and miles from the next café.
Stock a cool bag or 12V fridge for perishables, along with high-protein snacks like nuts, bars, and jerky. A travel kettle or camping stove opens the door to proper meals, and even a tin of soup or noodles feels like luxury on a cold night.
Don’t forget the basics!
- Water (at least 2 litres per day)
- A reusable mug
- Cutlery
- A bowl
Some drivers also pack sachets of coffee, instant porridge, or seasoning to spice things up.
These small comforts are often overlooked. However, they make excellent gifts for lorry drivers who spend long stretches on the road.
Bedding and sleep comfort
If you’re tramping, sleep is your fuel, and poor sleep makes long drives harder and more dangerous. A well-kitted sleeping area helps you rest properly and wake up ready for the road.
- A quality sleeping bag
- Pillow
- Blackout curtains (make a huge difference)
- Earplugs
- An eye mask (or even a white noise app to help block out noisy lay-bys)
Don’t overlook a spare blanket or a fitted sheet to cover your bunk, keeping your bed setup clean and comfy can improve your mood, energy and even your safety. For those sleeping in their cabs, sleep gear also counts among thoughtful lorry driver gifts that show you care about their rest.
Clothing and personal hygiene
It’s hard to stay comfortable or focused if you’re cold, damp or feeling unclean. Packing the right extras can keep you fresh and focused from one job to the next.
Pack spare workwear, waterproofs, a warm hoodie and a towel. Trainers or sliders are good for rest stops, and quick-dry fabrics save space and time.
In your washbag, keep:
- A toothbrush
- Deodorant
- Wipes
- A razor
- Some toilet paper
Add hand sanitiser and flip-flops if you’re planning to use communal showers.
Weather kit and seasonal extras
British weather can flip in minutes, and being caught out in the wrong gear is more than just uncomfortable; it can be dangerous. A compact weather kit helps you adapt quickly and stay safe in all conditions.
For winter, carry:
- A windscreen scraper
- De-icer spray
- Thermal gloves
- A warm hat
It’s also worth keeping a shovel and sand or cat litter in case you get stuck on icy roads.
In summer? A cap, sunscreen, and portable fan go a long way during long, hot waits.
If you regularly cross into Europe, remember some countries require winter tyres or snow chains, pack accordingly. Many of these seasonal items double as clever HGV accessories for UK or cross-border hauliers.
Loading and unloading equipment
Even if loading isn’t your main job, a little kit can help speed things up. It also shows you’re prepared, which goes a long way with depot staff and site managers.
For loading and unloading carry:
- Gloves,
- Steel-toe boots
- Load ratchet straps
- Hi-vis gear
A portable step or pallet truck might also come in handy, especially at smaller depots.
Before you leave, always check your load is secure, even if it’s a short hop between stops. Loose cargo is one of the most common causes of delivery delays and accidents.
Cleaning and cab organisation
You spend most of your day in your cab, so it’s worth keeping it clean and functional. It makes eating, sleeping, and even driving feel less like a chore.
Use dashboard wipes and cloths to keep surfaces dust-free, and bin bags for any rubbish.
A small broom or handheld vacuum helps with dirt tracked in from your boots, and storage boxes, hanging seat organisers, and crates keep everything in reach.An air freshener or microfibre cloth for the windows can also make your space feel more like home. From storage hacks to dashboard wipes, these are great ideas if you’re browsing for lorry driver gifts with a personal touch.
Entertainment and wellbeing
Life on the road can feel repetitive, so it’s important to bring things that lift your mood. When you’re stuck in a lay-by or waiting at a depot, entertainment helps pass the time.
Pack headphones and pre-download podcasts, audiobooks, or playlists.
A Kindle, sketchpad, or journal offers a screen-free break, and puzzles or games help kill time too.Don’t underestimate physical wellbeing either, resistance bands, a quick stretch, or a walk around the lay-by can refresh your body and mind. Even small moments of rest and joy matter, so whether it’s podcasts, books or fitness bands, entertainment gear is one of the more underrated truck driver accessories on the road.
Long-haul tramping extras
If you’re regularly away for days at a time, consider indulging yourself beyond the basics. These extras won’t just keep you comfortable, they can make the road feel more like home.
Drivers often carry:
- Fold-out chairs
- Travel kettles
- Extra cutlery
- Mini mirrors
- USB fan or heater
- A small TV
- Phone stands
- Dry food containers
- Extra socks
Find reliable carriers and cut your costs with Haulage Exchange
Sign upFrequently asked questions
What are the legal requirements for UK HGV driver equipment?
You must carry your CPC card, tacho card, and any relevant documents for the load you’re hauling. Hi-vis gear is recommended, and some international routes require extra items like warning triangles or breathalysers.
What should I pack for bad weather or breakdowns?
In winter, bring a foil blanket, gloves, warm clothes, and a tow rope or high-grip mat. All year round, carry a hi-vis vest, torch, warning triangle, and a power bank.
How can I improve sleep in my cab?
Block out noise and light using curtains, earplugs, or white noise apps. A proper duvet, pillow, and spare blanket will also help you get quality rest between shifts.
Welcome to This Week in Freight, your go-to source for the latest haulage and road freight news and advice in the UK.
Choosing the right truck for your fleet just got easier. This week’s leading analysis breaks down the best truck brands for UK transport businesses in 2025, comparing reliability, servicing coverage, safety tech and whole-life costs — giving operators a clear view of what truly performs on UK roads.
We also take a deep dive into ISO accreditations and how they’re becoming a key differentiator in winning bigger, better, and more sustainable contracts across the industry.
And in London, new data confirms that tough HGV visibility rules are working — with sharp drops in serious collisions involving vulnerable road users.
Alongside the big stories, we’re covering major sustainability developments across Europe, from investment in heavy-duty charging corridors to new long-range electric trucks and biomethane breakthroughs. Plus, practical guides on bulk haulage, EU licence reforms, AI adoption in logistics, and the latest industry trials from DPD and Mercedes.
Let’s get into the week’s biggest shifts shaping UK and EU road transport.
🛣️ UK’s best trucks for 2025

Choosing the right truck brand shapes uptime, running cost and fleet performance — and the gaps between manufacturers are widening.
Our new guide breaks down how Scania, Volvo, Mercedes, DAF and MAN stack up for fuel economy, servicing coverage, safety tech and driver comfort.
It also explains which brands suit long-haul, regional or vocational work, plus the latest on diesel, electric and gas powertrains. A must-read for anyone planning their 2025 fleet strategy.
→ See how the major brands compare.
🏙️ Safer streets thanks to London’s HGV rules

New TfL collision data released for Road Safety Week shows a sharp drop in serious injuries involving HGVs and vulnerable road users since London introduced the Direct Vision Standard.
The figures confirm that improved cab visibility and blind-spot elimination are preventing the most severe incidents. With mandatory permits, roadside checks and upgraded safety systems now in force, London’s model is influencing EU design rules too.
→ Read the full findings behind the safety gains.
🏅 ISO basics for UK operators

Winning contracts increasingly depends on proving reliability — and ISO accreditations are becoming the benchmark.
In our new guide, we explain how ISO 9001, 14001, 45001, 27001, 39001 and more help hauliers cut risk, improve safety, strengthen sustainability reporting and meet client expectations.
It also covers costs, timelines, audits and how ISO compares with FORS and DVSA Earned Recognition, giving operators a clear path to certification.
→ Get the full breakdown on key ISO standards.
Also worth a read
- ♻️ Here’s a practical guide to walking floor trailers, showing how operators can expand into bulk and waste haulage while staying compliant and safe.
- 🇪🇺 New EU driving-licence reforms will reshape recruitment, minimum ages and cross-border enforcement for hauliers by 2029.
- 🚧 Humber Bridge’s new ANPR tolling system has been pushed to February 2026, delaying fee increases but promising smoother traffic once live.
- 🎖️ MoD examiners are being drafted in to cut HGV test delays, adding thousands of extra tests and easing pressure on vocational test centres.
- 🚚 Mercedes’ new “Safety Truck” shows how advanced detection, braking and fatigue-monitoring tech is becoming a direct driver of fleet profitability.
- 🤖 New research shows most fleet managers believe AI will boost efficiency and cut emissions, with adoption accelerating across the industry.
Sustainability updates
From new charging corridors to cleaner truck technology, here’s what’s driving the shift towards lower-carbon haulage right now.
- ♻️ A new EU deal paves the way for 44-tonne zero-emission trucks in cross-border operations, giving operators more payload flexibility as part of wider Weights & Dimensions reforms.
- 🔌 The EU is investing €600m to build megawatt-class charging corridors and hydrogen stations across major freight routes, accelerating long-haul decarbonisation.
- 🌱 IVECO’s S-Way CNG has set a new benchmark by travelling over 1,000 km on a single refill, showcasing biomethane as a viable low-carbon alternative for long-haul.
- ⚡ Renault Trucks has unveiled new electric models spanning 12-tonne city trucks to 600-km long-haul tractors, expanding zero-emission options across all segments.
- 🚚 DPD is beginning a long-term trial of the Mercedes-Benz eActros 300 lowliner to understand real-world eHGV performance on double-deck trailer routes.
- 🏴 Zemo Partnership will lead a £1m Welsh Government programme to fast-track commercial vehicle decarbonisation through real-world fleet collaboration.
Find reliable carriers and cut your costs with Haulage Exchange
Sign upChoosing the right truck brands for your fleet shapes cost, reliability, and how your business performs on busy UK roads. A strong truck manufacturer helps you control downtime, support drivers, and stay ahead of new transport rules.
In this guide, we’ll compare the main lorry manufacturers operating in the UK and explain how each one fits different transport operations. We’ll also share clear guidance on cost, servicing, powertrains, and what to check before choosing a model for long-term use.
What we’ll cover
Fleets, bookings, subcontractors, compliance & payments.
With HX, you can manage them all in one place.What matters when choosing truck brands in the UK
The right truck brand supports your daily work, not just your long-term plans.
Operators look at servicing coverage, running cost, safety, and compliance before committing to any model.
Uptime and servicing
Uptime has a direct effect on customer commitments. A good support network helps you avoid delays, missed slots, and lost revenue.
When deciding between truck brands, you should check:
- Distance to approved workshops
- Parts availability
- Breakdown response
- Access to night or weekend servicing
Reliable support from the lorry manufacturer also helps you maintain a strong compliance record during DVSA inspections.
Fuel and running cost
Fuel remains the biggest pressure on budgets. Even small improvements matter over the life of a vehicle.
When deciding between lorry brands and models, you should look at:
- Real-world diesel performance
- Tyre choice
- Drivetrain efficiency
- Weight
- Aerodynamics
Fuel also links to emissions. Many fleets track their environmental footprint, which is why HGV carbon output now influences buying decisions for long-term contracts.
Driver comfort and safety
Drivers perform better when they work in a comfortable cab. Good layouts reduce fatigue, and stable handling builds confidence during long shifts.
Safety systems add another layer of protection. Modern ADAS tools help drivers avoid hazards, stay alert in traffic, and handle sudden events on busy roads.
Compliance
Compliance rules affect everything from access to city centres to contract requirements. Trucks that meet these rules early help fleets avoid penalties and save time.
When deciding between lorry manufacturers, you should consider:
- Euro 6(e) standards
- ULEZ access
- Conspicuity markings and safety visibility rules
- Future emissions targets
Some also review how different models affect their record under the operator licence, especially when managing multiple depots.
Costs play a part too, so topics like HGV road tax and long-term budgeting often shape the final decision.
The leading truck brands in the UK and where they fit best
Choose the badge that fits the job, not the marketing line.
Below is a practical look at how each major truck manufacturer performs in real UK operations, so you can match strengths to the work you actually run.
Scania

Scania is known for fuel-efficient long-haul performance. It suits operators who run high-mileage motorway work or predictable trunking routes.
Drivers value Scania for comfort and visibility. Both help reduce fatigue during extended shifts.
Scania’s aerodynamic cabs and predictive systems support strong fleet fuel efficiency, which helps cut long-term running cost.
Volvo Trucks
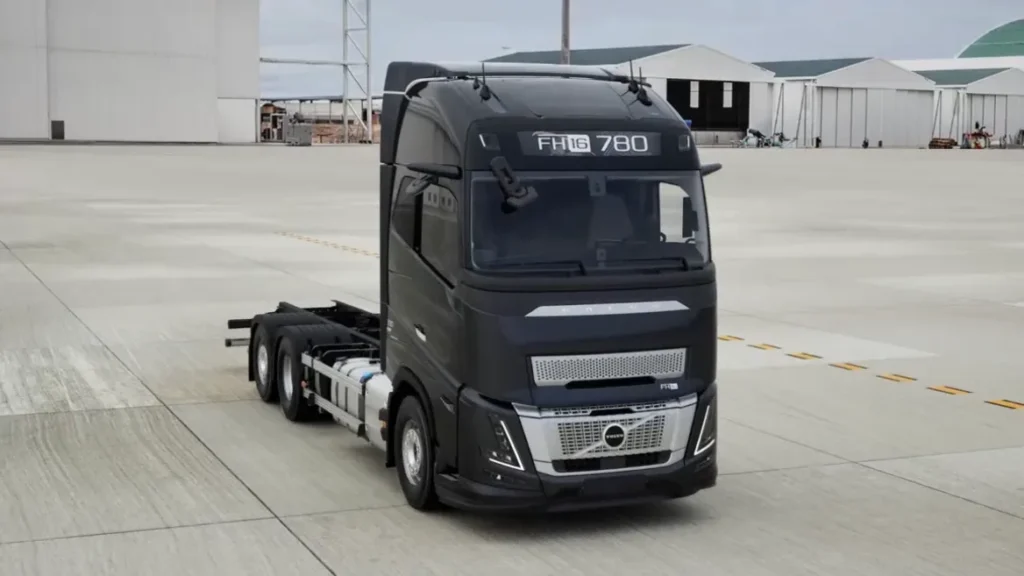

Volvo offers a balanced range of diesel, gas, and electric models. The FH covers long-haul work, while the FE and FM ranges suit regional and urban deliveries.
Safety tech is a standout feature. Volvo’s tools support drivers in traffic, on tight corners, and in low-visibility conditions. This makes it a common choice for fleets focusing on safety performance.
Mercedes-Benz Trucks
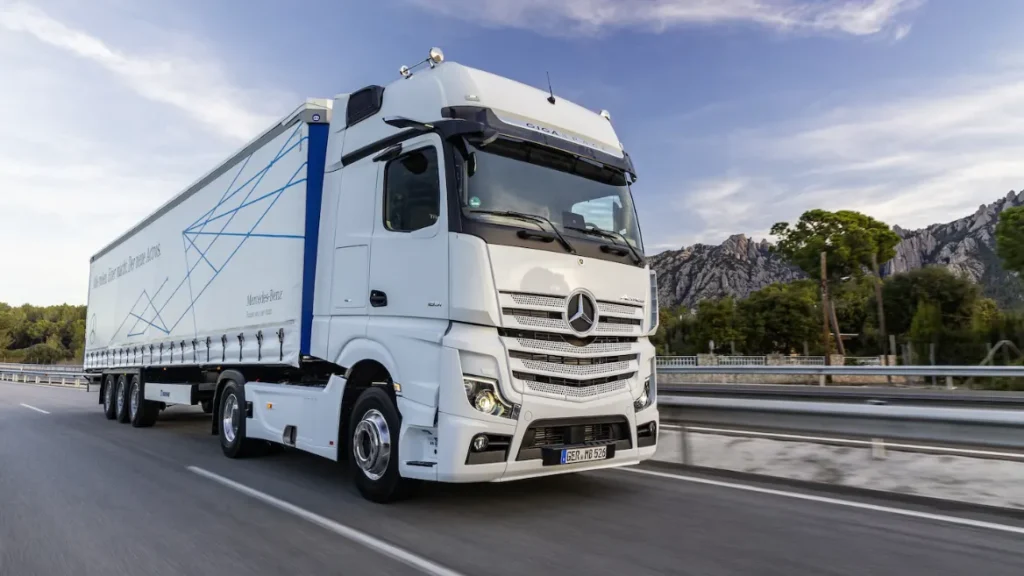

Mercedes works well in cities and busy regional areas. Its cab layouts offer clear visibility, and its safety systems help drivers manage hazards in tight urban streets.
The eActros supports fleets running short delivery routes with depot charging. Operators that handle multi-stop deliveries or city contracts often prefer Mercedes for its comfort and predictable servicing.
DAF
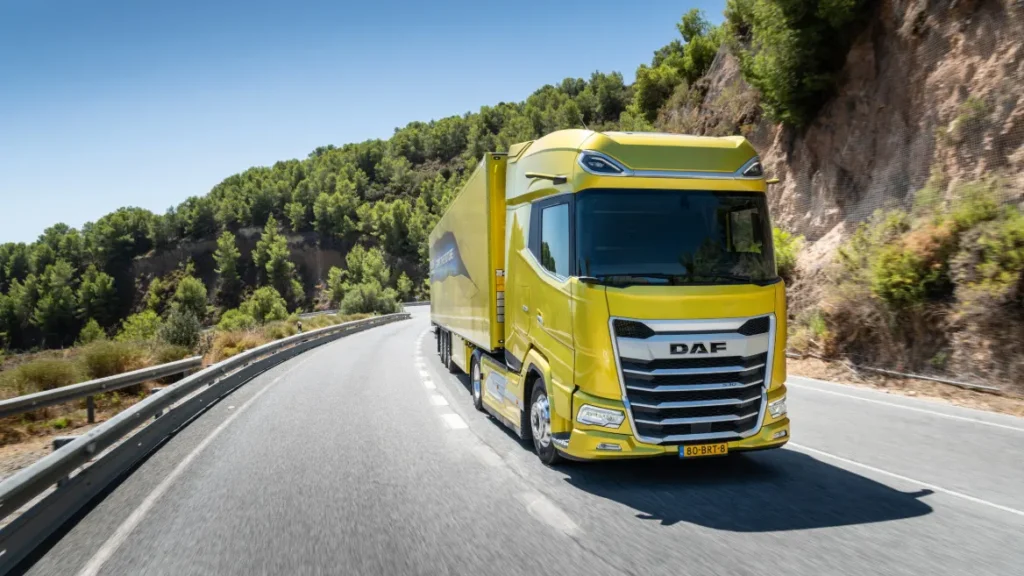

DAF offers one of the strongest servicing networks in the UK. This matters for operators with depots in different regions or fleets working across multiple counties.
DAF suits general haulage, regional distribution, and multi-driver operations. Its cabs offer simple layouts that work well for varied use.
MAN

MAN suits fleets running mixed operations. The TGX and TGM ranges offer comfortable cab layouts and predictable fuel use.
MAN supports a wide range of body types, which makes it useful for construction, waste, tanker, and regional distribution work. This flexibility helps operators that run mixed-duty schedules.
Matching truck types to UK transport operations
Selecting the right model matters as much as selecting the right truck brand.
UK fleets rely on three main truck types to cover long-haul, regional, and vocational work.
Tractor units (4×2 and 6×2)
Tractor units handle the heaviest loads in UK haulage. They support 44-tonne operations under lorry size regulations and work best for trunking, container movements, pallet networks, and supermarket deliveries.
Rigid trucks (7.5t to 26t)
Rigid trucks support regional deliveries, municipal duties, and food service work. Many new drivers start with these vehicles as part of their path to become a HGV driver, especially in urban and multi-drop roles.
Vocational trucks
Vocational operations rely on specialist chassis for tippers, mixers, waste vehicles, and recovery trucks. These vehicles handle varied body types and higher stress levels.
Discussions about future regulations and combinations often reference longer heavier vehicles (LHVs), especially for vocational roles with specialist payload demands.
Powertrains: diesel, gas, BEV and alternative fuels
Powertrain choice shapes your fuel strategy and future planning. Each option supports different types of UK routes.
Diesel
Diesel remains dominant for long-distance work because of range and reliability. Many fleets now use compatible renewable blends such as HVO biofuel to reduce emissions while keeping existing routes unchanged.
Electric
Electric trucks work well on predictable urban and regional routes. Depot charging fits these patterns because the truck returns to base after each shift.
Electric models run quietly, which suits night-time delivery windows.
Gas and hybrid
Gas trucks work well on fixed routes with access to refuelling points. They offer lower emissions for operators running closed-loop deliveries.
Hybrids serve a small part of the market, mostly for urban operations. Availability varies widely by truck brand.
Future alternatives
Hydrogen development continues, and test units appear more often across Europe. These models could suit heavier long-distance work in the future.
Sustainability planning in the sector aligns with long-term frameworks such as EBMPS, which guide operators on environmental targets and fleet transition planning.
Operating costs and lifecycle value
Operating cost shapes long-term fleet decisions. It affects fuel spend, repair planning, driver satisfaction, and resale value.
Fuel use and long-term running cost
Fuel performance differs by model and route type. Tractor units covering long-haul work show the clearest gaps in mpg. Even small improvements matter when trucks run hundreds of miles each day.
Fleets replacing older or used HGVs usually gain improved fuel returns, cleaner emissions, and more predictable servicing patterns. These gains support better planning for contracts that demand tight delivery windows or strong environmental performance.
Consistent fuel performance also stabilises margins in sectors that hold seasonal fluctuations or operate under fixed-rate agreements.
Maintenance and downtime
Reliable maintenance support helps fleets control downtime and avoid unexpected delays. Operators look for dependable workshop coverage, good parts availability, and predictable repair times.
Telematics helps here. Many fleets use connected data to plan inspections, track component wear, and monitor engine performance. These tools support better fleet management, especially when operating mixed fleets across several depots.
Good support also protects drivers, who rely on consistent vehicle performance to complete their shifts safely and without disruption.
Warranty and resale
Warranties protect operators from unexpected mechanical costs. Some extend them across driveline or full-vehicle coverage to keep budgets stable during slower periods.
Resale value shapes long-term cost. Higher-value truck brands help operators recover more when selling or trading in older models at the end of a contract.
Finance agreements also influence planning. Operators often review warranty coverage, residual value, and length of ownership when securing HGV finance, especially for fleets that refresh vehicles every few years.
A simple process to shortlist the right truck brands
Choosing the right vehicle starts with understanding how each model fits the work you handle. This simple process helps operators compare options clearly and make informed decisions.
Step 1: Match routes to vehicle types
Your main route structure shapes your buying decisions. Long-distance fleets need stable mpg and driver comfort. Regional fleets need flexibility. Vocational fleets need durable chassis that handle higher stress and site access.
Understanding route patterns helps operators avoid mismatched vehicles that cost more to run or maintain.
Step 2: Compare whole-life cost
Whole-life cost includes fuel performance, maintenance, warranty, and resale value. This view gives a clearer picture than relying on purchase price alone.
Analysing these costs together helps operators build stable budgets and avoid surprises later in a truck’s lifecycle.
Step 3: Gather driver and workshop feedback
Drivers offer real insights on comfort, handling, and fatigue. Workshop teams understand servicing patterns, part availability, and long-term reliability trends.
Collecting feedback from both groups gives a more complete view of how each model performs across daily operations.
Step 4: Trial before buying
Most truck brands offer demo vehicles. Testing them on real routes helps you compare mpg, comfort, visibility, and drivability.
These trials highlight differences that don’t always show up in spec sheets or brochures.
Step 5: Check compliance fit
Compliance influences long-term performance. Trucks must support emissions rules, safety requirements, and reliable maintenance records.
This is where reliable servicing helps fleets stay on track during DVSA inspections, as well as new visibility and emissions rules across major cities.
Final thoughts
Choosing the right truck brand helps fleets protect uptime, manage fuel spend, and improve the driving experience. The best options balance reliability, comfort, and predictable servicing. Each lorry manufacturer offers something different, so the right choice depends on your routes, the type of work you handle, and your long-term plans.
By reviewing servicing coverage, comparing whole-life cost, and trialling models on real routes, operators can choose truck types that support stable margins and strong performance across the year.
A structured approach makes the decision easier, especially as technology, emissions expectations, and business pressures evolve. Pick the lorry brand that aligns with your operation today and gives you the flexibility to adapt in the years ahead.
Find reliable carriers and cut your costs with Haulage Exchange
Sign upFrequently asked questions
Which truck brands are most reliable?
Scania, Volvo, Mercedes, DAF, and MAN all deliver strong reliability when serviced correctly. Reliability depends on route type, maintenance access, and how the vehicle is driven.
Are electric trucks suitable for long-distance work?
Electric trucks work best on regional and urban routes with predictable distances and depot charging. Long-distance operations still lean toward diesel until charging networks expand.
What affects running cost differences between brands?
Fuel performance, servicing patterns, tyre selection, and residual value all influence running cost. Driver behaviour also shapes long-term fuel use and component wear.
Which brands offer the best servicing coverage?
DAF has wide coverage across the UK. Mercedes, Volvo, Scania, and MAN also support service networks along major transport corridors and near key industrial hubs.
How should operators test new trucks before buying?
Use demo vehicles on real routes, compare mpg results, and gather feedback from both drivers and workshop teams. This helps confirm comfort, handling, and operating cost before committing.
In haulage and logistics, reliability is everything. Clients need confidence that their goods will be handled safely, securely and on time. But in a competitive market, how do you prove your business meets the highest standards?
That’s where ISO accreditations come in. They help logistics operators demonstrate professionalism, compliance and quality — all backed by internationally recognised standards.
Whether you’re a small haulage company tendering for new contracts or a national logistics provider looking to streamline operations, this guide explains everything you need to know about ISO accreditations for haulage, how they work and which ones matter most.
What we’ll cover
Fleets, bookings, subcontractors, compliance & payments.
With HX, you can manage them all in one place.What are ISO accreditations, and how do they work?
ISO stands for the International Organization for Standardization — a global, independent body that develops standards to ensure quality, safety and efficiency across almost every industry.
An ISO standard defines the best practice framework for a particular area (like environmental management or information security).
An ISO accreditation (also called certification) proves that your business meets that framework, verified through an external audit.
Accreditation involves:
- Implementing ISO requirements across your operations.
- Undergoing an independent audit by an accredited certification body.
- Maintaining compliance through regular reviews and recertification every few years.
ISO accreditations aren’t legally required, but many logistics clients, local authorities and national contracts expect suppliers to hold at least one — especially ISO 9001 and ISO 14001.
For hauliers, warehouses and depots, these accreditations provide structure, consistency and trust. They show customers and partners that you don’t just promise quality — you can prove it.
Why ISO accreditations matter for haulage and logistics
The haulage and logistics industry relies on coordination, compliance and communication. Any breakdown in these areas — a delayed shipment, an unsafe depot, or a lost data file — can have serious consequences.
ISO accreditations help to prevent those problems by creating repeatable, auditable processes across your organisation. But beyond compliance, they also deliver measurable business value:
- Win more contracts – Many large shippers and 3PLs only work with ISO-accredited suppliers.
- Reduce risk and liability – Standardised procedures minimise accidents, data breaches and errors.
- Improve efficiency – Better processes lead to fewer delays, smoother workflows and less waste.
- Strengthen reputation – ISO certification signals professionalism to customers, partners and haulage insurance providers.
- Support sustainability – Environmental and energy standards help reduce HGV carbon emissions and improve reporting.
For fleet operators, ISO standards complement other haulage accreditations such as FORS (Fleet Operator Recognition Scheme) or DVSA Earned Recognition. ISO provides the global framework; these national schemes build on it for specific transport compliance.
The ISO accreditations most relevant to logistics
There are more than 24,000 ISO standards worldwide, but only a handful directly impact the logistics sector. Below are the key ones every haulage or logistics company should know — along with how they apply in practice.
ISO 9001:2015 — Quality management
Focus: Quality, consistency and continual improvement.
ISO 9001 is the most widely recognised quality management standard in the world. It ensures that every part of your operation — from booking a load to delivering it — follows defined, repeatable procedures.
For logistics businesses, ISO 9001 proves you can meet customer expectations consistently. Many public sector and corporate contracts require it as a minimum.
It also encourages a culture of improvement: regular reviews, internal audits and data-driven decisions that help you refine performance year after year.
ISO 14001:2015 — Environmental management
Focus: Reducing environmental impact and promoting sustainability.
With growing emphasis on greener supply chains, ISO 14001 helps logistics companies monitor and minimise their environmental footprint.
This can include reducing fuel consumption, managing waste at warehouses and depots, improving route efficiency or switching to sustainable HGV fuels.
Holding ISO 14001 shows you take sustainability seriously — a major plus in tender evaluations and ESG reporting.
ISO 45001:2018 — Occupational health and safety
Focus: Protecting staff and reducing workplace incidents.
In haulage, safety isn’t optional. ISO 45001 provides a structured framework to identify hazards, assess risks and prevent accidents — whether in warehouses, on loading bays or during deliveries.
Accredited companies can demonstrate proactive management of driver fatigue, vehicle maintenance and manual handling risks. It also supports compliance with the UK Health and Safety at Work Act and can lower insurance premiums by reducing claim likelihood.
ISO 27001:2022 — Information security management
Focus: Protecting business and customer data.
Modern logistics is digital. You handle booking systems, payment data, telematics and customer records daily. ISO 27001 helps safeguard that information through strict controls on data access, storage and cyber-resilience.
For freight forwarders, transport management systems or SmartPay-enabled operators, this standard reassures partners that sensitive data is safe — essential in an age of rising cyber threats.
ISO 39001:2012 — Road traffic safety management
Focus: Reducing accidents and improving fleet safety.
ISO 39001 targets one of the biggest risks in haulage: road safety. It establishes procedures for monitoring driving performance, analysing incident data and improving journey planning.
Fleet managers use it to track key metrics such as collisions, near-misses and driver training. Implementing ISO 39001 demonstrates your commitment to keeping drivers — and other road users — safe.
ISO 28000:2022 — Supply chain security management
Focus: Protecting cargo and ensuring secure logistics.
This logistics ISO accreditation focuses on supply chain security — particularly for operators handling high-value or sensitive goods. It covers risk assessment, traceability, storage security and crisis response planning.
ISO 28000 accreditation is especially useful for international hauliers and logistics providers working with bonded warehouses, ports or airports.
ISO 50001:2018 — Energy management
Focus: Efficient energy use and cost reduction.
ISO 50001 helps logistics companies manage and reduce energy consumption across depots, fleets and buildings. It sets up systems to monitor fuel and electricity use, identify inefficiencies and measure improvements.
In an era of high fuel costs and carbon targets, this ISO standard supports both financial savings and sustainability credentials.
ISO 22301:2019 — Business continuity management
Focus: Keeping operations running during disruptions.
From IT failures to extreme weather, logistics operations face constant risk of disruption. ISO 22301 ensures your business can continue critical functions — like customer communication, load tracking and invoicing — during a crisis.
It helps you prepare contingency plans, backup systems and recovery processes to minimise downtime and maintain service reliability.
Supporting ISO standards for advanced logistics operators
Once the core standards are in place, some logistics businesses adopt additional ISO frameworks to strengthen customer relationships and governance:
- ISO 10002 – Customer satisfaction and complaints handling.
- ISO 26000 – Social responsibility guidance.
- ISO 31000 – Risk management principles and framework.
These aren’t mandatory but demonstrate maturity and leadership in how your business manages stakeholder expectations.

How to get ISO accredited for your haulage or logistics business
Getting ISO accredited can seem daunting, but it follows a clear process.
Most logistics companies complete their first accreditation within three to six months, depending on complexity.
Step-by-step process
- Choose the right standard(s). Start with the most relevant to your goals — usually ISO 9001 or ISO 14001 — and expand later.
- Conduct a gap analysis. Compare your current processes against the ISO requirements. Many certification bodies offer a pre-audit or consultancy service.
- Implement improvements. Create or update policies, training and documentation to align with the standard.
- Perform internal audits. Review your systems and fix any issues before the external audit.
- Undergo certification. An accredited body audits your business to confirm compliance. If successful, you receive your ISO certificate.
- Maintain and improve. ISO isn’t one-and-done — you’ll have annual surveillance audits and full recertification every three years.
Choosing a certification body
Always select a UKAS-accredited certification provider (the United Kingdom Accreditation Service).
UKAS accreditation ensures your certificate is genuine and internationally recognised.
Costs and practical considerations
The cost of ISO accreditation varies depending on your company’s size, number of sites and chosen standards.
Here are some typical ballpark figures for accreditation in the UK:
- Small operator (1–10 employees): £2,000–£4,000
- Medium operator (11–50 employees): £4,000–£7,000
- Large logistics group: £7,000–£10,000+
There’s also an ongoing annual audit or maintenance fee, usually lower than the initial certification cost.
While the upfront cost can feel significant, most logistics companies find ISO accreditation pays for itself through:
- Higher-value contracts
- Reduced accidents or claims
- Better efficiency and lower energy use
- Improved customer retention
Some regional business growth programmes or environmental funds may offer grants or subsidies to support ISO certification, especially for ISO 14001 or ISO 50001.
How ISO accreditations compare to other haulage standards
The UK transport industry already recognises several voluntary schemes, including:
Accreditation Focus Comparison to ISO FORS (Fleet Operator Recognition Scheme) Fleet safety, emissions and driver standards Practical fleet-based focus. ISO 9001 and 45001 complement it by adding structured management systems. DVSA Earned Recognition Compliance with vehicle maintenance and safety Focused on legal compliance; ISO adds a broader quality and process framework. RHA Audits / Logistics UK Schemes Operational and safety performance Often aligned with ISO principles — businesses holding both demonstrate strong governance. In short: FORS and similar schemes show compliance within UK transport; ISO proves excellence on a global scale.
Maintaining your ISO accreditation
Accreditation isn’t just a certificate — it’s an ongoing commitment.
To keep your ISO accreditation, you’ll need to:
- Conduct annual internal and external audits.
- Review KPIs and incident data for continual improvement.
- Keep documentation, training and safety records up to date.
- Re-certify every three years to demonstrate continued compliance.
Embedding ISO principles into everyday operations ensures your standards remain part of the business culture, not a one-off exercise.
Building a stronger, safer, smarter logistics business
For logistics professionals, ISO accreditations are more than a badge of honour. They’re a framework for running safer, more efficient and more sustainable operations.
From ISO 9001’s focus on quality to ISO 39001’s emphasis on road safety, these standards help transport companies of every size compete on professionalism — not just price.
And as sustainability and compliance expectations grow across the supply chain, ISO-accredited logistics businesses will stand out for the right reasons: trusted, transparent and ready for the future.
Find reliable carriers and cut your costs with Haulage Exchange
Sign upCommon questions about ISO accreditations
What is ISO accreditation in logistics?
It’s an independent certification proving your logistics operation meets globally recognised standards for quality, safety, or environmental performance.
Which ISO accreditations are most relevant for haulage companies?
The most common are ISO 9001, 14001, 45001 and 39001 — covering quality, environment, health & safety, and road safety.
How long does ISO accreditation take?
Usually between three and six months, depending on business size and readiness.
Is ISO accreditation mandatory for logistics businesses?
No, but many bigger clients, such as the public sector, require it as a condition of contract.
How often do you need to renew your ISO accreditation?
You’ll have surveillance audits each year and a full recertification every three years.
Thinking about a career move into freight brokering? Whether you’re already in logistics or starting fresh, becoming a freight broker in the UK opens up a world of opportunity.
In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know, from what the role involves to setting up your own freight brokerage business.
What we’ll cover
Fleets, bookings, subcontractors, compliance & payments.
With HX, you can manage them all in one place.What is a freight broker?
A freight broker is a middleman between shippers who need to move goods and carriers who can transport them.
They don’t handle the freight directly but use their network and industry know-how to match the right haulier with the right job.
If you’re still wondering what a freight broker is, think of them as the connector keeping supply chains moving efficiently.
The role of freight brokers in the supply chain
Freight brokers play an important part in optimising logistics. They negotiate rates, organise loads, and make sure goods are delivered on time.
While they don’t typically take responsibility for the cargo, unlike freight forwarders, understanding the differences between freight brokers and freight forwarders is important for knowing how each supports the supply chain.
Understanding the UK freight market
The UK’s freight market is fast-paced and highly competitive. With growing demand for domestic and international haulage, there’s definitely space for new brokers who can offer reliable, responsive service.
Digital tools and platforms like freight exchange networks have made the barrier to entry much lower.
Freight brokers in the UK often work across road, sea, and air logistics, giving them a flexible model. Most start with road freight, partnering with HGV drivers, smaller haulage companies and even courier companies. It’s also common to begin by helping companies secure return loads to increase profits and minimise empty journeys.
Regulatory considerations for UK freight brokering
Unlike in the US, you don’t need a freight broker licence in the UK—but that doesn’t mean there are no rules. You’ll need to follow standard trading and data protection regulations.
If you operate vehicles, you’ll also need an operator licence, but pure brokers don’t typically require one. That said, having proper contracts and freight agreements in place is important. So is understanding how the haulage industry works, from liability to scheduling.
If you’re brokering on behalf of multiple carriers, having the right freight forwarder insurance is essential.
How to become a freight broker
So, how do you become a freight broker in the UK? It’s more accessible than you might think, but success comes from preparation, professionalism, and building strong industry connections.
Let’s look at each of the major steps:
1. Education required
You don’t need a formal degree to get started, but a solid understanding of logistics and supply chain management helps. Many brokers come from haulage, admin, or customer service backgrounds. Courses in transport management or freight forwarding can give you an edge.
If you’re completely new to the industry, it’s worth learning the basics of how freight and transport bidding platforms work. These tools help you find loads, negotiate rates, and match carriers to jobs. Learning the tech side early sets you up for smoother operations later.
Even if you’re self-taught, staying informed is key. Keep an eye on freight regulations, market trends, and digital platforms. You can also read our other guides here on Freight Focus.

2. Licensing, bonding, and insurance essentials
Although UK freight brokers don’t require a specific broker licence, you should still operate as a registered business. That means choosing a business structure, registering with HMRC, and understanding your tax obligations. You’ll also want to consider professional indemnity insurance or carrier liability cover.
If you plan to handle freight directly or operate vehicles, you’ll need an operator licence. If you’re purely brokering freight between other parties, insurance is still vital to protect your business. Make sure your contracts are clear, especially regarding who is liable for damage or delays.
3. Setting up your freight brokerage business
You’ll need a business plan, basic tech setup, and a way to manage quotes, loads, and communications. Many brokers start from home, using load boards, freight exchange platforms, and spreadsheet tools to stay organised. As you grow, software like TMS (transportation management systems) can help automate operations.
Decide whether you’ll specialise: maybe small haulage, international freight, or urgent loads. You could focus on return loads to reduce waste and help carriers earn more per trip. The key is finding a niche and building a reputation for reliability.
At this stage, it’s also worth considering branding and marketing. A clear website, professional email, and reliable contact methods make you easier to trust. Being organised and responsive will set you apart and help you grow your freight forwarding company.
The key skills and qualities for success
- Time management and multitasking: You’ll often be managing several loads at once, fielding calls, updating clients, and handling admin. Staying organised helps avoid errors and keeps everyone on schedule. A reliable broker is a busy one, but never overwhelmed.
- Strong communication: Freight brokers need to be clear, concise, and responsive. Whether it’s confirming a booking or handling a delay, the way you communicate can build or break relationships. Carriers and shippers both appreciate someone who keeps them in the loop.
- Negotiation skills: Brokers sit between two parties with different goals—shippers want low costs, carriers want fair pay. It’s your job to find middle ground that works for both. Over time, good negotiators earn better margins and build stronger loyalty.
- Understanding how the industry works: You don’t need decades of experience, but you do need to understand how do freight brokers work, what makes a good route, and where delays typically happen. Knowing your stuff builds confidence and helps you solve problems fast. Clients trust brokers who know more than just the basics.
- Digital literacy and tech tools: From freight exchange platforms to tracking tools and CRMs, tech is central to modern freight brokering. The more comfortable you are with software, the smoother your operations will run. Automation also frees up your time for building relationships.
Best practices for freight brokers
If you want to stand out, focus on building long-term relationships, not just quick wins. Good brokers stay in regular contact with both shippers and hauliers, keeping communication clear and professional. This helps build trust, leading to repeat business.
Strong communication and negotiation skills are essential. That includes setting expectations, managing delays, and finding fair rates for everyone involved. Freight moves fast, and so should your updates.
When it comes to marketing your brokerage, don’t just rely on word-of-mouth. Like we said before, a clean, professional website and active presence on digital load boards make you easier to find. If you’re unsure where to start, look into platforms that support transport bidding for smaller jobs to build your network.
Freight brokerage startup costs
Starting a freight brokerage is relatively low-cost, especially if you’re working remotely or solo. You’ll need to budget for business registration, basic insurance, and tech tools. If you plan to grow, consider CRM software or even hiring admin support.
You make money by charging a margin between what the carrier gets and what the shipper pays. This margin varies, but the more efficient and trusted you are, the better rates you can negotiate. Learning how to become a freight broker agent can also be a stepping stone if you want to gain experience before launching your own company.
It’s also important to keep track of taxes, invoice terms, and late payment risks. Cash flow can be tight in the early months, so set clear payment terms and keep records. As your business scales, outsourcing bookkeeping may save you time and stress.
Challenges in freight brokering
Every job has its hurdles, and freight brokering is no exception. From carrier no-shows to last-minute cancellations, things don’t always go to plan. Staying calm and finding quick solutions is part of the job.
Brokers also face the challenge of keeping both shippers and carriers happy, while still protecting their own margins. It’s a balancing act that takes time to get right. If you’re wondering how to become a broker for freight and actually thrive, knowing the common pitfalls is a good place to start.
Common mistakes and how to avoid them
- Poor communication: Missed updates or unclear instructions can quickly damage trust with carriers and clients. Always confirm key details in writing and follow up regularly to keep everyone informed.
- Overpromising: Taking on too much too soon can lead to failed deliveries and missed deadlines. Start small, know your limits, and scale your workload as your systems and network grow.
- Relying on one client or carrier: Without a diverse network, one cancellation could disrupt your entire week. Spread your workload across multiple contacts to keep your business stable and flexible.
- Bad record-keeping: Failing to track quotes, contracts, or delivery notes can cause billing errors and disputes. Use simple spreadsheets or digital tools to stay organised and keep everything in one place.
- Not setting clear terms: Skipping formal agreements leads to confusion about responsibility, payment, or delivery expectations. Always outline who’s responsible for what before a job begins, and stick to written terms.
Future trends in freight brokering
Digital tools are reshaping the industry, and that’s good news for new brokers. Platforms now use automation, instant pricing, and real-time tracking to streamline freight matching. If you’re learning how to become a freight broker UK, it’s smart to stay ahead of the tech curve.
Sustainability is also becoming a bigger priority. Brokers who can optimise routes and reduce empty miles—like through return loads—will be more valuable. Clients want partners who help them meet green goals.
Lastly, demand for transparency is rising. Shippers expect live updates, reliable service, and easy communication. Brokers who offer that will likely stand out from the crowd.
Find reliable carriers and cut your costs with Haulage Exchange
Sign upFrequently asked questions
What makes a freight broker successful?
A successful freight broker builds strong relationships, communicates clearly, and consistently delivers value. It’s not just about moving loads, it’s about being reliable, responsive, and resourceful.
How profitable is a freight brokerage?
Freight brokering can be very profitable, especially if you operate efficiently and build a loyal customer base. Margins vary, but with low overheads and repeat business, brokers can earn a strong income.
How do I get customers as a freight broker?
Start by networking with carriers and shippers, joining online load boards, and offering your services on freight exchange platforms. Word-of-mouth is powerful, but so is having a professional presence online.
Welcome to This Week in Freight, your go-to source for the latest haulage and road freight news and advice in the UK.
Black Friday is coming — and so is the pressure. Ecommerce sales are forecast to hit £10.3bn, with order volumes up nearly 19%, putting 3PLs and warehouse operators under immense strain. We explore how the industry’s preparing for its biggest week of the year.
Also in this week’s edition: a record 23% rise in UK EV charge points, a practical guide to buying a used HGV without costly surprises, and new insight on freight crime, underground cold storage, and seasonal demand management.
💥 Ecommerce faces its biggest test yet

Online order volumes are set to rise by 18.6% this Black Friday, with shoppers expected to spend £10.3bn across the week, according to warehouse software provider Mintsoft.
For ecommerce sellers and 3PLs, that means pressure on fulfilment, delivery, and customer service like never before. From forecasting demand to avoiding costly mistakes, logistics leaders share how to prepare for the sector’s busiest week of the year — and why collaboration and transparency are key to surviving the surge.
→ Read the full Black Friday report.
🚛 How to buy a used HGV with confidence

Buying a used HGV can be a smart way to grow your fleet — but only if you know what to look for.
Our latest guide covers every step, from checking emissions compliance and ownership records to calculating the true cost of ownership.
It also includes a post-purchase checklist and advice on avoiding common pitfalls, ensuring your next truck is reliable, compliant, and fit for the road ahead.
→ Get the complete used HGV buying guide.
⚡ A new EV charger every 33 minutes

The UK’s public EV charging network has expanded by 23% in the past year — the equivalent of one new charger every 33 minutes.
With over 86,000 chargers now available, the government and private sector are racing to keep up with demand from both drivers and fleets.
New planning reforms and major investments from ChargeUK, Vauxhall and Gridserve are ensuring access for renters, rural areas, and freight operators alike.
→ Read the full EV infrastructure update.
Also worth a read
- 🚛 Learn how to forecast demand, scale your fleet, and keep deliveries on track when seasonal peaks hit the road freight sector.
- 🧊 Cold storage moves underground as M&M Quality Solutions opens a subterranean logistics hub — reshaping the future of temperature-controlled freight.
- 🕵️♂️ What a $100m Louvre jewellery heist can teach the industry about preventing freight fraud and cargo theft.
- 🛡️ With freight crime soaring, experts say driver safety and secure parking must move to the top of the logistics agenda.
Find reliable carriers and cut your costs with Haulage Exchange
Sign upBuying a used HGV can be one of the smartest ways to grow your fleet without overspending. But with so many factors to consider – from emissions standards to ownership checks – it’s easy to make an expensive mistake.
In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know before you buy a second-hand HGV, from understanding your operational needs to calculating long-term costs.
What we’ll cover
Fleets, bookings, subcontractors, compliance & payments.
With HX, you can manage them all in one place.Buy new or second-hand – which is right for your business?
When it comes to expanding your fleet, deciding between a brand-new and a used HGV comes down to your priorities: cost, reliability, and flexibility.
Both have clear advantages — but also some trade-offs.
Buying a new HGV:
- Comes with a full manufacturer warranty and no prior wear.
- You’ll get access to a wider range of different lorry types.
- Meets the latest emissions and freight transport standards out of the box.
- Often includes telematics, safety tech, and low-emission compliance for cold chain transport and urban work.
- But you’ll pay a premium, wait longer for delivery, and face faster depreciation in the first few years.
Buying a used HGV:
- Much lower upfront cost, freeing cash for upgrades or extra drivers.
- Immediate availability — ideal for meeting new haulage contracts quickly.
- Easier to finance through finance or short-term leasing.
- May require checks on emissions, maintenance, and compliance to avoid future costs.
In short, buying new suits operators focused on long-term efficiency and minimal downtime. Buying a second-hand HGV suits those expanding fast or balancing cash flow.
1. Understand what you need before you buy
Before looking at vehicles, think about how your used HGV will be used day to day. The right choice depends on the type of work, routes, and loads you handle.
Things to consider:
- Operation type: Long-haul, regional, or last-mile deliveries.
- Body style: Rigid, tractor unit, or specialist vehicle such as a walking floor lorry.
- Payload and axle configuration: Match capacity to your contracts, not your ambitions.
- Fuel and emissions: Choose Euro VI to avoid daily ULEZ charges and lower HGV carbon emissions.
- Future-proofing: Consider compatibility with HVO fuel or hybrid systems.
Many buyers over-purchase – paying for capacity they rarely use. Focus on trucks and lorry brands that suit your routes and haulage contracts.

2. Check legal and identity documents
Before money changes hands, confirm the truck’s legal status and identity. A few quick checks can save you from disputes and hidden costs later.
Here’s what to check:
- VIN and registration: Cross-check on DVSA and HPI databases.
- MOT history: Look for consistent mileage and any recurring advisories.
- Finance and theft records: Use an HPI or NMR check to confirm the vehicle’s clear of outstanding finance.
- Imports: Confirm NOVA registration and a valid Certificate of Conformity or IVA approval.
- Ownership chain: Match the V5C with the seller’s business name and VAT status.
If you’re adding the truck to an operator’s licence, make sure it’s listed promptly to stay compliant with traffic commissioner requirements. Missing paperwork or gaps in history are warning signs.
3. Inspect the mechanical and technical condition
A used HGV that looks clean on the yard might still hide issues. A professional inspection is well worth the fee.
What to look for:
- Engine leaks or unusual smoke.
- Clutch wear and brake performance.
- Suspension and steering play.
- Corrosion on the chassis or cab.
- Tyre age (must be under 10 years on steering axles) and tread depth (minimum 1mm).
- Warning lights or diagnostic codes showing emission or DPF faults.
If possible, get an independent HGV mechanic to inspect the vehicle or run a full pre-purchase inspection. Ask for service records and brake test reports to confirm the truck’s been properly maintained.
You can also check that the truck meets DVSA annual test standards before completing the sale. A small cost upfront can save thousands in repairs later.
4. Stay compliant with UK and local standards
Regulations affect where and when you can operate a used HGV. Make sure the vehicle meets current and future requirements before you commit.
Emission and safety standards to check:
- ULEZ and Clean Air Zones: Vehicles must be Euro VI to avoid daily fees in cities like London, Birmingham, and Manchester.
- Direct Vision Standard (DVS): HGVs entering London need at least a 3-star rating or a Progressive Safe System retrofit.
- Weight and axle limits: Keep within legal limits for your configuration.
- Safety equipment: Cameras, conspicuity markings, and side guards might be mandatory in some areas.
Buying a cheaper, older truck can look like a saving, but the wrong emissions class can quickly eat into your profit through daily charges.
5. Calculate the total cost of ownership (TCO)
The sticker price only tells part of the story. To know the true cost of your used HGV, calculate its total cost of ownership over three to five years.
Cost Area What to Consider Fuel economy Compare Euro V vs Euro VI efficiency. Maintenance Check availability and price of spare parts. Insurance Factor in HGV insurance and risk profile. Telematics Integration with fleet management tools. Road tax Include annual HGV road tax costs. Resale value Euro VI trucks hold their value better. A slightly higher upfront price can mean lower running costs and downtime. Make sure you calculate everything before you commit.
6. Research the seller and buy with confidence
Not all sellers offer the same level of transparency. Whether you’re buying a used HGV from a dealer, auction, or private seller, trust and documentation matter.
Dealers and sellers:
- Franchised dealers: Usually offer warranties and service records.
- Independent traders: May have competitive prices but check documentation carefully.
- Fleet disposals: Often well-maintained and come with complete service histories.
Questions to ask:
- Can I see full service and repair records?
- Has the truck been used for light haulage or heavy work?
- Is the mileage consistent across MOT, tachograph, and service records?
- What’s the VAT and ownership status?
Use secure payment methods and always get a formal invoice for your used HGV. Avoid rushed transactions or pressure to pay deposits upfront.
What to do after buying a used HGV
Once the sale’s complete, a few administrative steps keep you on the road legally.
Post-purchase checklist:
- Transfer the V5C registration to your name or company.
- Add the vehicle to your operator’s licence.
- Set up HGV insurance and schedule routine maintenance.
- Pay HGV road tax and keep the receipt for records.
- Fit telematics or cameras to integrate with your yard management systems.
- If needed, refurbish the body, repaint the cab, or add safety features.
Some buyers also arrange HGV financing for upgrades for their used HGV, such as retrofitting camera systems or emissions controls.
Common buying mistakes to avoid
A few oversights can turn a good deal into a financial headache. Here are the mistakes to avoid when buying a used HGV:
- Not inspecting the vehicle in person.
- Failing to check emissions compliance before buying.
- Ignoring gaps in the service history.
- Buying without checking for outstanding finance.
- Forgetting to budget for the first maintenance cycle.
If the price seems too good to be true, it usually is.
Building a reliable, future-ready fleet
A well-chosen used HGV can serve your business for years. Think beyond today’s contracts and plan for long-term flexibility. Whether you’re just starting your haulage company, growing your operation, or specialising in niche freight, the right purchase supports your goals without overstretching your budget.
Used trucks play an important role in modern freight transport, helping operators balance costs while maintaining reliability. With the right approach, you can expand safely, reduce supply chain vulnerability, and strengthen your overall supply chain optimisation strategy.
And remember: the best truck isn’t just the one that’s cheapest today, but the one that fits your routes, haulage loads, and compliance obligations tomorrow.
Find reliable carriers and cut your costs with Haulage Exchange
Sign upFrequently asked questions
What’s the average mileage for a reliable used HGV?
Most operators look for trucks with under 500,000 miles, but mileage matters less than maintenance. A well-serviced high-mileage truck can outperform a neglected one.
Are used HGVs still subject to ULEZ or Clean Air Zone charges?
Yes. Unless they meet Euro VI standards, older trucks pay daily fees in most cities. Always check local authority websites before purchase.
Can I buy a used HGV through finance?
Yes. Many buyers use finance agreements to spread costs. Check interest rates, balloon payments, and ownership terms before committing.
What’s better for my business: a rigid or articulated truck?
It depends on your operation. Rigids suit regional and urban work, while tractor units offer flexibility for long-distance haulage contracts and different lorry types.
How can I reduce my running costs after buying?
Use telematics to track fuel use and schedule maintenance. Switching to HVO fuel where compatible can also reduce emissions and operating costs.
Welcome to This Week in Freight, your go-to source for the latest haulage and road freight news and advice in the UK.
Amazon’s at it again — this time with smart glasses for delivery drivers. Are they the next big leap for hands-free logistics, or just surveillance in disguise?
Meanwhile, the EU is tightening ADR inspections with new risk classifications that could change how carriers transport dangerous goods, and HVO fuel is taking centre stage as a cleaner, drop-in diesel alternative.
Also in this week’s round-up: AI that drivers actually want in their cabs, the safest new truck stop in the UK, and the Dutch cities leading Europe’s zero-emission freight revolution.
👓 Smart glasses for drivers?

Amazon’s new smart glasses promise safer, hands-free deliveries — projecting routes, parcel data and hazard alerts directly in drivers’ view.
But critics warn the tech could bring tighter targets and new levels of workplace surveillance.
As AI-powered wearables enter logistics, the line between innovation and intrusion is blurring.
→ See how Amazon’s pilot could reshape driver life.
🧯 EU steps up ADR safety checks

The EU has approved new ADR inspection rules introducing a unified checklist, tougher penalties, and shared responsibility across the supply chain.
From June 2026, hauliers, loaders, and even consignees must follow stricter documentation and training standards for dangerous goods.
→ Find out what the new directive means for your compliance plans.
🌱 HVO fuel powers the road to net zero
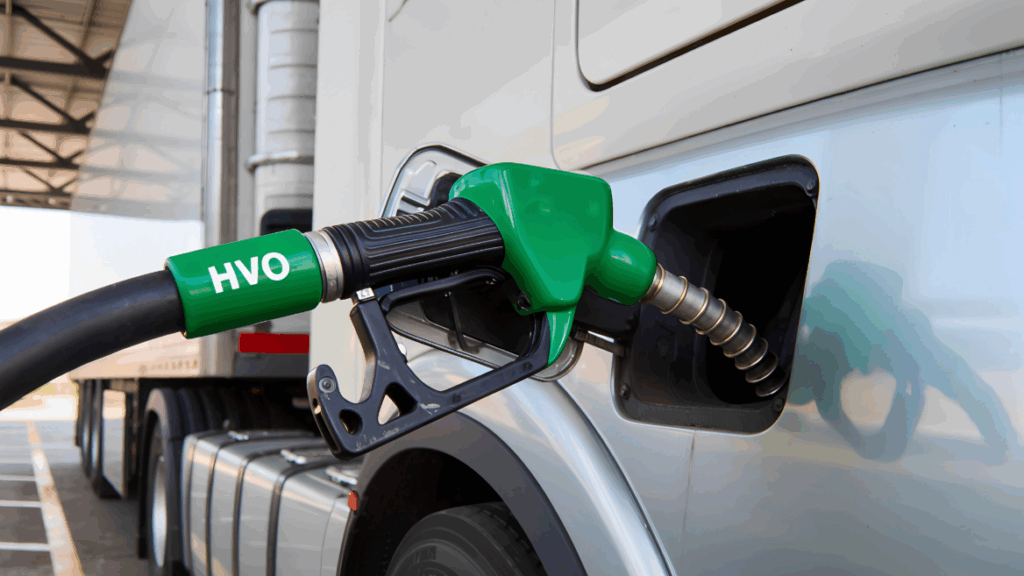

HVO fuel is gaining ground as a drop-in diesel alternative that cuts emissions by up to 90%.
Compatible with most modern HGVs, it offers fleets a quick, low-risk route to cleaner operations without new infrastructure.
With prices set to fall as production scales, it’s becoming a realistic step towards decarbonising UK haulage.
→ Get the complete guide to HVO fuel for your fleet.
Also worth a read
- 📡 ADAS tech is transforming HGV safety, helping drivers avoid fatigue, cut collisions and meet new EU safety standards.
- 💷 Fuel duty could rise again as experts warn the Autumn Budget may reverse the 5p cut and explore pay-per-mile road charges.
- 📱 LeShuttle Freight has launched a new Driver Companion app, keeping drivers informed, connected and rewarded throughout their journeys.
- 🛑 Sutterton truck stop in Lincolnshire has earned Park Mark Freight status, joining the UK’s safest and best-equipped sites for drivers.
- 🤖 Most UK truck drivers support AI in cabs — but only if video footage isn’t stored, highlighting the balance between safety and privacy.
Sustainability news
Here are this week’s big developments across road haulage sustainability:
- ⚡ DFDS has deployed the UK’s first government-backed electric HGV, marking a milestone for the ZenFreight consortium and the country’s zero-emission freight rollout.
- 🇳🇱 Dutch zero-emission zones are driving record EV adoption, with electric truck registrations up nearly 190% year on year as logistics firms embrace cleaner fleets.
- 💨 Biomethane deserves a bigger role in decarbonising haulage, according to a new industry report urging policy changes to extend fuel duty discounts and boost investment.
Find reliable carriers and cut your costs with Haulage Exchange
Sign upHaulage businesses across the UK are under pressure to cut emissions and move towards cleaner energy. Heavy goods vehicles are still largely diesel-powered, but that’s beginning to change. HVO fuel offers hauliers a simple way to reduce emissions without replacing their fleet or infrastructure.
In this guide, we’ll look at what HVO fuel is, how it works, and what it means for HGV fleets today.
What we’ll cover
Fleets, bookings, subcontractors, compliance & payments.
With HX, you can manage them all in one place.What is HVO fuel?
HVO fuel, short for hydrotreated or hydrogenated vegetable oil, is a renewable diesel alternative made from waste fats and vegetable oils. It’s part of a group known as paraffinic diesels, which are synthetically produced from renewable materials rather than crude oil.
Unlike traditional biodiesel, HVO fuel doesn’t contain fatty acid methyl esters (FAME). This makes it more stable, cleaner burning, and less prone to issues like oxidation or water contamination. Because it’s a “drop-in” fuel, operators can use it in existing diesel engines with no modifications.
You’ll also hear it called renewable diesel, green diesel, or HVO diesel, but they all refer to the same thing.
How HVO fuel is made
HVO fuel is produced through a process called hydrotreatment. Waste oils and animal fats are purified, then treated with hydrogen at high temperatures. This process removes oxygen and impurities, creating a high-quality hydrocarbon fuel almost identical to fossil diesel.
The hydrotreatment process includes two main stages:
- Pre-treatment: Feedstocks such as used cooking oil and animal fat waste are filtered and cleaned.
- Hydrotreatment and isomerisation: Hydrogen reacts with the oils to form pure hydrocarbons that mimic diesel in structure and performance.
Because the process is tightly controlled, the result is a consistent, clean, and stable fuel. HVO can be stored for up to 10 years, compared to around one year for regular diesel.
HVO vs biodiesel vs fossil diesel
Property Fossil diesel Biodiesel (FAME) HVO fuel Feedstock Crude oil Vegetable/animal fats Waste oils & fats Stability 1 year Poor Up to 10 years Cetane number ~51 50–65 70–90 Emissions High CO₂ & NOx Moderate Up to 90% CO₂ reduction Compatibility Full Limited blends 100% drop-in Cold weather performance Average Poor Excellent (-27°C CFFP) While biodiesel can only be blended in small percentages, HVO can replace diesel entirely. It burns more cleanly, gives better cold starts, and resists degradation in storage.
Environmental and performance benefits of HVO fuel for haulage
For the haulage industry, HVO fuel offers a rare combination of cleaner emissions, improved reliability, and straightforward adoption. It helps fleets meet sustainability goals without sacrificing performance or uptime.
HVO for haulage is a genuine drop-in fuel — it can be used immediately in most existing diesel engines with no mechanical modifications or new infrastructure. Major manufacturers such as DAF, Volvo, Scania, MAN, Mercedes-Benz, Iveco, and Renault Trucks have approved its use, alongside equipment makers like Caterpillar and John Deere.
This compatibility makes it a practical, low-risk switch for fleets that want to cut emissions quickly while keeping operations running as normal.
When used as a full replacement for diesel, HVO can cut lifecycle CO₂ emissions by up to 90%. These reductions come from its renewable origins and the cleaner way it burns inside engines. It’s also free from sulphur, aromatics, and FAME, which makes it far more stable than conventional fuels.
1. Cleaner emissions and sustainability gains
HVO releases far fewer pollutants than fossil diesel, producing lower levels of nitrogen oxide (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and carbon monoxide (CO). These reductions help improve air quality, particularly in cities and logistics hubs where HGVs often operate.
Because it’s made from waste oils, fats, and residues, HVO supports a circular approach to fuel production. Every litre reused helps divert waste from landfill or incineration, making it a strong fit for circular economy logistics models.
For haulage operators working under emissions reporting frameworks or haulage contracts that require sustainability metrics, these measurable carbon savings can make a real difference. The fuel’s performance has also been independently verified under the Renewable Transport Fuel Obligation (RTFO), reinforcing its role in helping businesses transition to lower-carbon operations.
2. Reliable performance and engine health
HVO isn’t just about lowering emissions. Its high cetane number, usually between 70 and 90, provides faster ignition and more complete combustion. That leads to quieter operation, improved fuel efficiency, and less engine wear over time.
Because it burns cleaner and contains no FAME, there’s less soot formation and injector fouling, meaning longer service intervals and fewer maintenance callouts. Fleets that switch to HVO often report cleaner filters and lower emissions test readings, even under heavy use.
3. Cold weather stability and storage life
For operators storing bulk fuel at depots, reliability in all conditions is critical. HVO maintains consistent performance in cold weather, with a Cold Filter Plugging Point (CFFP) as low as -27°C. This means trucks can operate efficiently throughout the winter without waxing or fuel flow issues.
Another major advantage is HVO’s storage stability. While mineral diesel begins to degrade after a year, HVO can be stored safely for up to 10 years with minimal risk of oxidation or microbial growth. This makes it ideal for large depots, standby generators, and seasonal operations.
Add to that its non-toxic and biodegradable nature, and you’ve got a renewable fuel that’s both safer to handle and easier to manage long term.

Cost and availability
Right now, HVO fuel costs around 10–15% more than standard diesel. Prices vary by supplier and region, mainly due to feedstock costs and limited UK production capacity.
Despite this, many hauliers see the higher cost as a trade-off for long-term savings. HVO helps fleets stay compliant with emissions regulations and can lower costs tied to maintenance and carbon reporting.
UK suppliers such as Crown Oil, Prema Energy, and Your NRG distribute HVO nationwide, though supply can be limited in rural areas. Over time, as production expands, prices are expected to narrow.
Supply and sourcing in the UK
The UK’s growing demand for renewable diesel has outpaced local production. At present, most HVO for haulage is imported from large-scale European producers like Neste, where it’s refined using waste oils and animal fats. Once processed, it’s distributed to UK suppliers who manage regional delivery networks.
Feedstocks used to make HVO include used cooking oils, tallow, and vegetable residues, all of which would otherwise become waste. These materials are cleaned, treated, and refined into a consistent, paraffinic diesel with the same energy density as standard fuel.
Because the availability of these feedstocks depends on agricultural and food industry output, prices can fluctuate. Seasonal shifts in supply and competition from other sectors also influence wholesale cost. As more waste-derived inputs and refining capacity come online, these costs are expected to stabilise.
Certification and fuel quality
To verify that HVO fuel is sustainable and responsibly sourced, hauliers should look for certification from schemes like ISCC (International Sustainability & Carbon Certification) or RFAS (Renewable Fuel Assurance Scheme). These certifications confirm that the fuel is:
- Derived from traceable, waste-based feedstocks rather than palm oil.
- Verified for greenhouse gas reductions across its full lifecycle.
- Fully compliant with the UK’s Renewable Transport Fuel Obligation (RTFO).
Most certified suppliers provide a Proof of Sustainability (POS) document, which details the origin and production route of each batch.
Choosing certified HVO protects businesses from reputational risks and supports genuine carbon reduction efforts.
Choosing the right supplier
For hauliers planning a transition to renewable fuel, supplier choice matters. When sourcing HVO, it’s worth checking:
- Whether the product is ISCC- or RFAS-approved and palm-free.
- If the supplier can offer consistent volumes across multiple depots.
- Lead times for bulk orders and whether prices are fixed or indexed.
- Blending options, in case you plan to phase adoption gradually.
Because HVO has a long storage life, some operators choose to buy in bulk when prices are favourable. This approach also minimises delivery emissions and administrative time.
Understanding where your HVO fuel comes from not only helps control costs but also reinforces your business’s environmental commitment. In an industry where traceability and compliance are becoming central to tendering and haulage contracts, sourcing the right supplier can make a measurable difference.
Challenges and considerations
While HVO for haulage is one of the most promising low-carbon fuels available, there are challenges.
- Availability: Distribution networks are still expanding, so not all regions have consistent supply.
- Feedstock sourcing: Quality can vary depending on supplier, especially if non-certified palm oil is used.
- Certification: Look for ISCC or RFAS certification to confirm waste-derived origins.
- Cost: Still higher than diesel, though this gap is closing.
HVO isn’t completely carbon neutral. Emissions vary depending on how it’s made and transported, but it’s a major step towards decarbonisation while maintaining performance.
HVO vs electric vehicles for haulage
Electric trucks are often seen as the long-term solution for road transport, but they’re not yet practical for every operation. HVO fuel offers an immediate alternative that works with existing diesel fleets.
Electric HGVs require new infrastructure, higher upfront costs, and more downtime for charging. HVO can be used today with no major changes, making it an ideal transitional fuel while electrification develops.
Many operators now use a mix of both—electric for urban deliveries and HVO for long-haul routes where range and payload matter.
Regulations and the future of renewable fuels
Government initiatives like the Renewable Transport Fuel Obligation (RTFO) are pushing UK businesses to adopt low-carbon fuels. As part of the move toward net zero, liquid fuels like HVO are gaining traction in the haulage and logistics sectors.
Many fleets also face new reporting pressures under Scope 3 emissions standards. Switching to renewable fuels supports those sustainability metrics while maintaining performance and reliability.
Over the next decade, the UK is expected to expand on-road access for HVO, especially for commercial transport. More suppliers are entering the market, and growing investment in renewable production means better supply and pricing in the near future.
How to switch to HVO fuel
Switching to HVO is straightforward. Here’s how hauliers can do it:
- Check your engine manufacturer’s approval list for HVO compatibility.
- Choose a certified, palm-free HVO supplier.
- Clean existing diesel tanks if switching entirely to avoid residue contamination.
- Consider a blended approach initially (e.g. 20–50%) before moving to 100%.
- Track fuel usage and emission savings for reporting.
There’s no downtime or complex installation. You can simply fuel up and go.
The road ahead for haulage
HVO isn’t just a greener alternative—it’s a practical way to keep your business compliant, efficient, and future-ready. It gives operators a bridge between today’s diesel fleets and tomorrow’s zero-emission technology.
As government targets tighten and customer expectations shift, hauliers using HVO fuel can show real progress on sustainability without disrupting operations.
From long-haul freight to haulage return loads, HVO provides flexibility, reliability, and a clear route to cleaner transport.
Find reliable carriers and cut your costs with Haulage Exchange
Sign upFrequently asked questions
Can I use HVO fuel in any diesel engine?
Yes. Most modern diesel engines are compatible with HVO, but it’s always worth checking the manufacturer’s guidance.
Is HVO available at UK fuel stations?
Public access is limited, but it’s widely available through commercial suppliers in bulk quantities.
Does HVO affect fuel economy?
Performance and fuel economy are very similar to fossil diesel, often with smoother combustion and less noise.
Is HVO better for the environment than biodiesel?
Yes. It produces lower emissions and is more stable, so it stores better and performs consistently.
Can HVO be mixed with diesel?
Yes. It can be blended in any ratio, although you’ll see the biggest benefits from using pure HVO (HVO100).
Add-ons
Support
About
2000 - 2025. Transport Exchange Group Ltd, Reg No. 3464353 © E&OE